Identification of a Novel, Small Molecule Partial Agonist for the Cyclic AMP Sensor, EPAC1
- PMID: 28331191
- PMCID: PMC5428521
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-00455-7
Identification of a Novel, Small Molecule Partial Agonist for the Cyclic AMP Sensor, EPAC1
Abstract
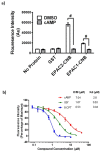
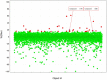
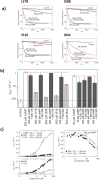
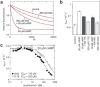
Screening of a carefully selected library of 5,195 small molecules identified 34 hit compounds that interact with the regulatory cyclic nucleotide-binding domain (CNB) of the cAMP sensor, EPAC1. Two of these hits (I942 and I178) were selected for their robust and reproducible inhibitory effects within the primary screening assay. Follow-up characterisation by ligand observed nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) revealed direct interaction of I942 and I178 with EPAC1 and EPAC2-CNBs in vitro. Moreover, in vitro guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) assays revealed that I942 and, to a lesser extent, I178 had partial agonist properties towards EPAC1, leading to activation of EPAC1, in the absence of cAMP, and inhibition of GEF activity in the presence of cAMP. In contrast, there was very little agonist action of I942 towards EPAC2 or protein kinase A (PKA). To our knowledge, this is the first observation of non-cyclic-nucleotide small molecules with agonist properties towards EPAC1. Furthermore, the isoform selective agonist nature of these compounds highlights the potential for the development of small molecule tools that selectively up-regulate EPAC1 activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Sands WA, Woolson HD, Milne GR, Rutherford C, Palmer TM. Exchange protein activated by cyclic AMP (Epac)-mediated induction of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS-3) in vascular endothelial cells. Molecular and cellular biology. 2006;26:6333–6346. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00207-06. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI121012/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- PG/10/26/28303/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- BB/D015324/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- PG/15/15/31316/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- FS/17/12/32703/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

