Spotlight on blisibimod and its potential in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus: evidence to date
- PMID: 28331294
- PMCID: PMC5357079
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S114552
Spotlight on blisibimod and its potential in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus: evidence to date
Abstract
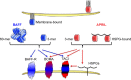
B cells in general and BAFF (B cell activating factor of the tumor necrosis factor [TNF] family) in particular have been primary targets of recent clinical trials in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In 2011, belimumab, a monoclonal antibody against BAFF, became the first biologic agent approved for the treatment of SLE. Follow-up studies have shown excellent long-term safety and tolerability of belimumab. In this review, we critically analyze blisibimod, a novel BAFF-neutralizing agent. In contrast to belimumab that only blocks soluble BAFF trimer but not soluble 60-mer or membrane BAFF, blisibimod blocks with high affinity all three forms of BAFF. Furthermore, blisibimod has a unique structure built on four high-affinity BAFF-binding peptides fused to the IgG1-Fc carrier. It was tested in phase I and II trials in SLE where it showed safety and tolerability. While it failed to reach the primary endpoint in a recent phase II trial, post hoc analysis demonstrated its efficacy in SLE patients with higher disease activity. Based on these results, blisibimod is currently undergoing phase III trials targeting this responder subpopulation of SLE patients. The advantage of blisibimod, compared to its competitors, lies in its higher avidity for BAFF, but a possible drawback may come from its immunogenic potential and the anticipated loss of efficacy over time.
Keywords: APRIL; B cells; BAFF; blisibimod; lupus.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Blisibimod for treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus: with trials you become wiser.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2016;16(5):723-33. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2016.1169270. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27051973 Review.
-
Phase III trial results with blisibimod, a selective inhibitor of B-cell activating factor, in subjects with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.Ann Rheum Dis. 2018 Jun;77(6):883-889. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213032. Epub 2018 Mar 21. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018. PMID: 29563108 Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus patients with the BAFF antagonist "peptibody" blisibimod (AMG 623/A-623): results from randomized, double-blind phase 1a and phase 1b trials.Arthritis Res Ther. 2015 Aug 20;17(1):215. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0741-z. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26290435 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Therapeutic targeting of the BAFF/APRIL axis in systemic lupus erythematosus.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2014 Apr;18(4):473-89. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2014.888415. Epub 2014 Feb 13. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2014. PMID: 24521424 Review.
-
Inhibition of B cell activating factor (BAFF) in the management of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2017 Jun;13(6):623-633. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2017.1291343. Epub 2017 Feb 15. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28164726 Review.
Cited by
-
New Pathways and Therapeutic Targets in Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis.J Neuromuscul Dis. 2018;5(3):265-277. doi: 10.3233/JND-170294. J Neuromuscul Dis. 2018. PMID: 30010142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A narrative review of potential drug treatments for nephritis in children with IgA vasculitis (HSP).Clin Rheumatol. 2023 Dec;42(12):3189-3200. doi: 10.1007/s10067-023-06781-8. Epub 2023 Sep 27. Clin Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 37755547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Update on Targeted Treatment of IgA Nephropathy: An Autoimmune Perspective.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 23;12:715253. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.715253. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34497518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Clinical Features and Serum Biomarkers in Identifying Patients with Incomplete Lupus Erythematosus at Higher Risk of Transitioning to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Current Perspectives.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Feb 18;15:1133-1145. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S275043. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35210816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biologics in the Treatment of Lupus Erythematosus: A Critical Literature Review.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Jul 18;2019:8142368. doi: 10.1155/2019/8142368. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31396534 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lanzavecchia A. Antigen-specific interaction between T and B cells. Nature. 1985;314(6011):537–539. - PubMed
-
- Mamula MJ, Lin RH, Janeway CA, Jr, Hardin JA. Breaking T cell tolerance with foreign and self co-immunogens. A study of autoimmune B and T cell epitopes of cytochrome c. J Immunol. 1992;149(3):789–795. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

