Investigating the expression, effect and tumorigenic pathway of PADI2 in tumors
- PMID: 28331341
- PMCID: PMC5352236
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S92389
Investigating the expression, effect and tumorigenic pathway of PADI2 in tumors
Abstract
Background: Peptidylarginine deiminase (PAD) catalyzes the conversion of arginine residues to citrulline residues, termed citrullination. Recent studies have suggested that PAD isoform 2 (PADI2) plays an important role in tumors, although its tumorigenic effect and mechanism are largely unknown.
Materials and methods: Immunohistochemistry and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) were used to investigate the expression level of PADI2 in various tumor tissues and patient blood samples, respectively. MNK-45 and Bel-7402 tumor cell lines originating from gastric and liver tumors, respectively, were treated with anti-PADI2 siRNA, and the subsequent cell proliferation, apoptosis and migration were observed. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) arrays, including Cancer PathwayFinder, Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes, p53 Signaling Pathway, Signal Transduction Pathway and Tumor Metastasis PCR arrays, were used to investigate the tumorigenic pathway of PADI2 in the siRNA-treated tumor cells. This analysis was verified by real-time PCR.
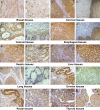
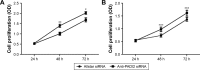
Results: Immunohistochemistry detected significantly increased expression of PADI2 in invasive breast ductal carcinoma, cervical squamous cell carcinoma, colon adenocarcinoma, liver hepatocellular carcinoma, lung cancer, ovarian serous papillary adenocarcinoma and papillary thyroid carcinoma samples. ELISA detected a twofold increase in PADI2 expression in the blood of 48.3% of patients with liver cancer, 38% of patients with cervical carcinoma and 32% of patients with gastric carcinoma. Increased apoptosis and decreased cell proliferation and migration were observed in the anti-PADI2 siRNA-treated MNK-45 cells, and increased cell proliferation and migration and decreased apoptosis were observed in the treated Bel-7402 cells with suppressed PADI2 expression. PCR arrays and real-time PCR detected significantly decreased CXCR2 and EPO expression in the MNK-45 cells and Bel-7402 cells, respectively, with the anti-PADI2 siRNA treatments.
Conclusion: PADI2 expression is increased in many types of tumor tissues and patient blood samples. PADI2 may advance abnormal cell behavior in gastric cancers by mediating CXCR2, a well-known gene that stimulates cell proliferation and invasion. However, PADI2 might have deleterious effects on tumor growth and metastasis in liver tumor cells by regulating the expression of EPO, a gene with controversial functions in tumor growth. The results suggest that the effect of PADI2 on tumorigenesis is multifactorial, depending on the tumor type.
Keywords: CXCR2; EPO; PADI2; pathway; tumorigenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures






References
-
- Pritzker LB, Nguyen TA, Moscarello MA. The developmental expression and activity of peptidylarginine deiminase in the mouse. Neurosci Lett. 1999;266(3):161–164. - PubMed
-
- Arita K, Hashimoto H, Shimizu T, Nakashima K, Yamada M, Sato M. Structural basis for Ca(2+)-induced activation of human PAD4. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2004;11(8):777–783. - PubMed
-
- Chavanas S, Méchin MC, Nachat R, et al. Peptidylarginine deiminases and deimination in biology and pathology: relevance to skin homeostasis. J Dermatol Sci. 2006;44(2):63–72. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

