Pregnancy suppresses neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury in rats through the inhibition of TNF-α
- PMID: 28331359
- PMCID: PMC5349853
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S121810
Pregnancy suppresses neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury in rats through the inhibition of TNF-α
Abstract
Purpose: Pregnancy-induced analgesia develops during late pregnancy, but it is unclear whether this analgesia is effective against neuropathic pain. The detailed molecular mechanisms underlying pregnancy-induced analgesia have not been investigated. We examined the antinociceptive effect of pregnancy-induced analgesia in a neuropathic pain model and the expression of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), Iba-1, and c-Fos in the spinal dorsal horn just before parturition.
Materials and methods: Female Sprague Dawley rats (200-250 g) were randomly assigned to one of four groups (pregnant + chronic constriction injury [CCI]; pregnant + sham injury; not pregnant + CCI; and not pregnant + sham injury). Separate groups were used for the behavioral and tissue analyses. CCI of the left sciatic nerve was surgically induced 3 days after confirming pregnancy in the pregnancy group or on day 3 in the not pregnant group. The spinal cord was extracted 18 days after CCI. TNF-α, GFAP, Iba-1, and c-Fos expression levels in the spinal dorsal horn were measured by Western blot analysis. Mechanical threshold was tested using von Frey filaments.
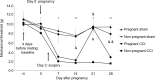
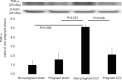
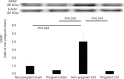
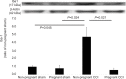
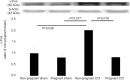
Results: The lowered mechanical threshold induced by CCI was significantly attenuated within 1 day before parturition and decreased after delivery. TNF-α expression in CCI rats was decreased within 1 day before parturition. Further, GFAP, Iba-1, and c-Fos expression in the spinal dorsal horn was reduced in the pregnant rats. Serum TNF-α in all groups was below measurable limits.
Conclusion: Our findings indicate that pregnancy-induced analgesia suppresses neuropathic pain through reducing spinal levels of TNF-α, GFAP, Iba-1, and c-Fos in a rat model of CCI.
Keywords: TNF-α; glial cell; neuropathic pain; pregnancy-induced analgesia.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effect of electroacupuncture on the expression of spinal glial fibrillary acidic protein, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta in chronic neuropathic pain rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2010 Feb;35(1):12-6. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2010. PMID: 20458900 Chinese.
-
Montelukast attenuates neuropathic pain through inhibiting p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor-kappa B in a rat model of chronic constriction injury.Anesth Analg. 2014 May;118(5):1090-6. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000000174. Anesth Analg. 2014. PMID: 24686047
-
Contralateral neuropathic pain and neuropathology in dorsal root ganglion and spinal cord following hemilateral nerve injury in rats.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008 May 20;33(12):1344-51. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181733188. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008. PMID: 18496347
-
Hyperbaric oxygenation therapy alleviates chronic constrictive injury-induced neuropathic pain and reduces tumor necrosis factor-alpha production.Anesth Analg. 2011 Sep;113(3):626-33. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e31821f9544. Epub 2011 May 19. Anesth Analg. 2011. PMID: 21596875
-
Repeated electroacupuncture treatment attenuated hyperalgesia through suppression of spinal glial activation in chronic neuropathic pain rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 Feb 21;18(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2134-8. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 29466978 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pregnancy ameliorates neuropathic pain through suppression of microglia and upregulation of the δ-opioid receptor in the anterior cingulate cortex in late-pregnant mice.J Anesth. 2024 Dec;38(6):828-838. doi: 10.1007/s00540-024-03402-9. Epub 2024 Sep 8. J Anesth. 2024. PMID: 39244720
-
[Effects of different materials for partial sciatic nerve ligation on glial cell activation in rat models of chronic constriction injury].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2020 Aug 30;40(8):1207-1212. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2020.08.20. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2020. PMID: 32895191 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Within and Beyond the Binary: Sex and Gender Differences in Pain and Alcohol Use Disorder.Curr Addict Rep. 2024 Feb;11(1):68-80. doi: 10.1007/s40429-023-00534-y. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Curr Addict Rep. 2024. PMID: 40747361 Free PMC article.
-
The Need to Consider Pregnancy As a Biological Variable to Reduce Preventable Suffering Related to Pregnancy.J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2021 Feb;30(2):260-264. doi: 10.1089/jwh.2020.8870. Epub 2020 Nov 20. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2021. PMID: 33216677 Free PMC article.
-
The analgesic effect of early hyperbaric oxygen treatment in chronic constriction injury rats and its influence on nNOS and iNOS expression and inflammatory factor production.Mol Pain. 2018 Jan-Dec;14:1744806918765837. doi: 10.1177/1744806918765837. Mol Pain. 2018. PMID: 29592784 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Woolf CJ, Mannion RJ. Neuropathic pain: aetiology, symptoms, mechanisms, and management. Lancet. 1999;353(9168):1959–1964. - PubMed
-
- Rice ASC, Hill RG. New treatments for neuropathic pain. Annu Rev Med. 2006;57:535–551. - PubMed
-
- Gallagher RM. Management of neuropathic pain: translating mechanistic advances and evidence-based research into clinical practice. Clin J Pain. 2006;22(1 Suppl):S2–S8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

