microRNA and thyroid hormone signaling in cardiac and skeletal muscle
- PMID: 28331574
- PMCID: PMC5359910
- DOI: 10.1186/s13578-017-0141-y
microRNA and thyroid hormone signaling in cardiac and skeletal muscle
Abstract
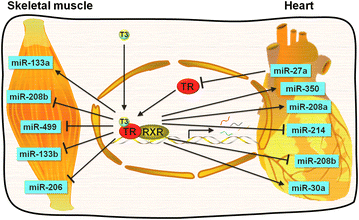
Thyroid hormone (TH) signaling plays critical roles in the differentiation, growth, metabolism, and physiological function of all organs or tissues, including heart and skeletal muscle. Due to the significant progress in our understanding of the molecular mechanisms that underlie TH action, it's widely accepted that TH signaling is regulated at multiple levels. A growing number of discoveries suggest that microRNAs (miRNAs) act as fine-tune regulators of gene expression and adds sophisticated regulatory tiers to signaling pathways. Recently, some pioneering studies in cardiac and skeletal muscle demonstrating the interplay between miRNAs and TH signaling suggest that miRNAs might mediate and/or modulate TH signaling. This review presents recent advances involving the crosstalk between miRNAs and TH signaling and current evidence showing the importance of miRNA in TH signaling with particular emphasis on the study of muscle-specific miRNAs (myomiRs) in cardiac and skeletal muscle. Although the research of the reciprocal regulation of miRNAs and TH signaling is only at the beginning stage, it has already contributed to our current understanding of both TH action and miRNA biology. We also encourage further investigations to address the relative contributions of miRNAs in TH signaling under physiological and pathological conditions and how a group of miRNAs are coordinated to integrate into the complex hierarchical regulatory network of TH.
Keywords: Heart; Skeletal muscle; Thyroid hormone; miRNA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interplay among miR-29 family, mineral metabolism, and gene regulation in Bos indicus muscle.Mol Genet Genomics. 2020 Sep;295(5):1113-1127. doi: 10.1007/s00438-020-01683-9. Epub 2020 May 22. Mol Genet Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32444960
-
MicroRNAs and thyroid hormone action.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021 Apr 5;525:111175. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2021.111175. Epub 2021 Jan 27. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 33515639 Review.
-
Thyroid Hormone-Regulated Cardiac microRNAs are Predicted to Suppress Pathological Hypertrophic Signaling.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014 Oct 20;5:171. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2014.00171. eCollection 2014. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014. PMID: 25368602 Free PMC article.
-
Systems biology approach identifies key regulators and the interplay between miRNAs and transcription factors for pathological cardiac hypertrophy.Gene. 2019 May 25;698:157-169. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.02.056. Epub 2019 Mar 5. Gene. 2019. PMID: 30844478
-
Novel Insight Into the Epigenetic and Post-transcriptional Control of Cardiac Gene Expression by Thyroid Hormone.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Aug 29;10:601. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00601. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 31555215 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hesperidin alleviates hypothyroidism-related cardiac dysfunction by targeting cardiac miRNAs, Nrf2/NF-κB signaling, oxidative stress and inflammation.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 2;16:1553992. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1553992. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40672362 Free PMC article.
-
Physiologic Significance of Epigenetic Regulation of Thyroid Hormone Target Gene Expression.Eur Thyroid J. 2020 May;9(3):114-123. doi: 10.1159/000506423. Epub 2020 Mar 24. Eur Thyroid J. 2020. PMID: 32523888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B regulates miR-208b-argonaute 2 association and thyroid hormone responsiveness in cardiac hypertrophy.Sci Signal. 2022 Apr 19;15(730):eabn6875. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.abn6875. Epub 2022 Apr 19. Sci Signal. 2022. PMID: 35439023 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Transcriptomic Interactomes of Noncoding RNAs in the Heart under Altered Thyroid Hormonal States.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 31;24(7):6560. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076560. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047531 Free PMC article.
-
Thyroid hormone activates Xenopus MBD3 gene via an intronic TRE in vivo.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2020 Jan 1;25(3):437-451. doi: 10.2741/4812. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2020. PMID: 31585895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yen PM. Physiological and molecular basis of thyroid hormone action. Physiol Rev. 2001;81:1097–1142. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources