The Efficiency of Diffusion Weighted MRI and MR Spectroscopy On Breast MR Imaging
- PMID: 28331671
- PMCID: PMC5351515
- DOI: 10.5152/tjbh.2014.2142
The Efficiency of Diffusion Weighted MRI and MR Spectroscopy On Breast MR Imaging
Abstract
The main purpose of breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in radiologically routine is to establish an imaging protocol that will create high quality images with a short period of time. Fort this purpose, an imaging protocol should include a conventional breast MRI and contrast enhanced sequences. Proton MR spectroscopy (MRS) and diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) are important MR techniques for evaluation to complicated breast lesions. In this article, we will evaluate that technical properties of the MRS and DWI as additional MR imaging.
Keywords: Breast; MR spectroscopy; diffusion weighted MRI.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
Figures
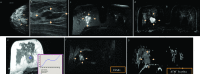
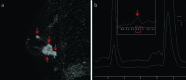
References
-
- Sardanelli F, Boetes C, Borisch B, Decker T, Federico M, Gilbert FJ, Helbich T, Heywang-Köbrunner SH, Kaiser WA, Kerin MJ, Mansel RE, Marotti L, Martincich L, Mauriac L, Meijers-Heijboer H, Orecchia R, Panizza P, Ponti A, Purushotham AD, Regitnig P, Del Turco MR, Thibault F, Wilson R. Magnetic resonance imaging of the breast: Recommendations from the EUSOMA working group. Eur J Cancer. 2010;46:1296–1316. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2010.02.015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ei Khouli RH, Jacobs MA, Mezban SD, Huang P, Kamel IR, Macura KJ, Bluemke DA. Diffusion-weighted imaging improves the diagnostic accuracy of conventional 3.0-T breast MR imaging. Radiology. 2010;256:64–73. http://dx.doi.org/10.1148/radiol.10091367. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Grenier P, Cabanis E, Laval-Jeantet M. MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: application to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders. Radiology. 1986;161:401–407. http://dx.doi.org/10.1148/radiology.161.2.3763909. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tan SLL, Rahmat K, Rozalli FI, Mohd-Shah MN, Aziz YF, Yip CH, Vijayananthan A, Ng KH. Differentiation between benign and malignant breast lesions using quantitative diffusion-weighted sequence on 3 T MRI. Clin Radiol. 2014;69:63–71. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.crad.2013.08.007. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kuhl CK. Concepts for differential diagnosis in breast MR imaging. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2006;14:305–328. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mric.2006.07.002. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
