Qualitative Assessment of the Symptoms and Impact of Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency (PEI) to Inform the Development of a Patient-Reported Outcome (PRO) Instrument
- PMID: 28332032
- PMCID: PMC5605612
- DOI: 10.1007/s40271-017-0233-0
Qualitative Assessment of the Symptoms and Impact of Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency (PEI) to Inform the Development of a Patient-Reported Outcome (PRO) Instrument
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic exocrine insufficiency (PEI) affects patients with chronic pancreatitis (CP) and cystic fibrosis (CF) who produce insufficient digestive pancreatic enzymes. Common symptoms include steatorrhoea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
Objective: The objective of the study was to develop and test the content validity of a patient-reported outcome (PRO) instrument assessing PEI symptoms and their impact on health-related quality of life.
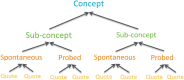
Methods: Instrument development was supported by a literature review, expert physician interviews (n = 10: Germany 4, UK 3, France 3), and exploratory, qualitative, concept-elicitation interviews with patients with CF and CP with PEI (n = 61: UK 29, Germany 18, France 14) and expert physicians (n = 10). Cognitive debriefing of the draft instrument was then performed with patients with PEI (n = 37: UK 24, Germany 8, France 5), and feasibility was assessed with physicians (n = 3). For all interviews, verbatim transcripts were qualitatively analysed using thematic analysis methods and Atlas.ti computerized qualitative software. All themes were data driven rather than a priori.
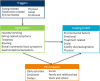
Results: Patient interviews elicited symptoms and impacts not reported in the literature. Six symptom concepts emerged: pain, bloating, bowel symptoms, nausea/vomiting, eating problems, and tiredness/fatigue. Six impact domains were also identified. A 45-item instrument was developed in English, French, and German for testing in cognitive debriefing patient interviews. Following cognitive debriefing, 18 items were deleted.
Conclusion: Rigorous qualitative patient research and expert clinical input supported development of a PEI-specific PRO with the potential to aid management and monitoring of unmet needs among patients with PEI. The next step is to perform psychometric evaluation of the resulting instrument.
Keywords: Chronic Pancreatitis; Cognitive Debriefing; Cystic Fibrosis; Expert Physician; Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding
This study was funded by Abbott.
Conflict of interest
Mr. Arbuckle, Ms. Bonner, and Ms. Williamson were contracted by Abbott as consultants to perform the research. Professors Lerch, Levy, Johnson, and Dominguez-Munoz and Drs. Connett and Staab were engaged as expert scientific advisors by Adelphi Values on behalf of Abbott and received honoraria for their participation. The authors declare there are no other competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Toouli J, et al. Management of pancreatic exocrine insufficiency: Australasian Pancreatic Club recommendations. Med J Aust. 2010;193(8):461–467. - PubMed
-
- Kahl S, et al. The effect of oral pancreatic enzyme supplementation on the course and outcome of acute pancreatitis: a randomized, double-blind parallel-group study. JOP. 2014;15(2):165–174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

