Xeno-free culture of human pluripotent stem cells on oligopeptide-grafted hydrogels with various molecular designs
- PMID: 28332572
- PMCID: PMC5362828
- DOI: 10.1038/srep45146
Xeno-free culture of human pluripotent stem cells on oligopeptide-grafted hydrogels with various molecular designs
Abstract
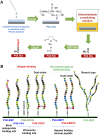
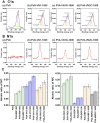
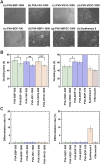
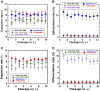
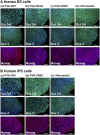
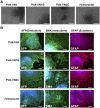
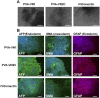
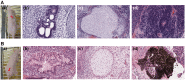
Establishing cultures of human embryonic (ES) and induced pluripotent (iPS) stem cells in xeno-free conditions is essential for producing clinical-grade cells. Development of cell culture biomaterials for human ES and iPS cells is critical for this purpose. We designed several structures of oligopeptide-grafted poly (vinyl alcohol-co-itaconic acid) hydrogels with optimal elasticity, and prepared them in formations of single chain, single chain with joint segment, dual chain with joint segment, and branched-type chain. Oligopeptide sequences were selected from integrin- and glycosaminoglycan-binding domains of the extracellular matrix. The hydrogels grafted with vitronectin-derived oligopeptides having a joint segment or a dual chain, which has a storage modulus of 25 kPa, supported the long-term culture of human ES and iPS cells for over 10 passages. The dual chain and/or joint segment with cell adhesion molecules on the hydrogels facilitated the proliferation and pluripotency of human ES and iPS cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Higuchi A. et al.. Biomaterials for the feeder-free culture of human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells. Chem. Rev. 111, 3021–3035 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Higuchi A. et al.. Design of polymeric materials for culturing human pluripotent stem cells: Progress toward feeder-free and xeno-free culturing. Prog. Polym. Sci. 39, 1348–1374 (2014).
-
- Takahashi K. et al.. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell. 131, 861–872 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Yu J. et al.. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science 318, 1917–1920 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Thomson J. A. et al.. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 282, 1145–1147 (1998). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

