Calmodulin is responsible for Ca2+-dependent regulation of TRPA1 Channels
- PMID: 28332600
- PMCID: PMC5362816
- DOI: 10.1038/srep45098
Calmodulin is responsible for Ca2+-dependent regulation of TRPA1 Channels
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Calmodulin is responsible for Ca2+-dependent regulation of TRPA1 Channels.Sci Rep. 2017 May 4;7:46588. doi: 10.1038/srep46588. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28471425 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
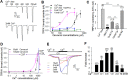
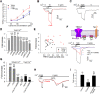
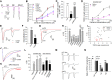
TRPA1 is a Ca2+-permeable ion channel involved in many sensory disorders such as pain, itch and neuropathy. Notably, the function of TRPA1 depends on Ca2+, with low Ca2+ potentiating and high Ca2+ inactivating TRPA1. However, it remains unknown how Ca2+ exerts such contrasting effects. Here, we show that Ca2+ regulates TRPA1 through calmodulin, which binds to TRPA1 in a Ca2+-dependent manner. Calmodulin binding enhanced TRPA1 sensitivity and Ca2+-evoked potentiation of TRPA1 at low Ca2+, but inhibited TRPA1 sensitivity and promoted TRPA1 desensitization at high Ca2+. Ca2+-dependent potentiation and inactivation of TRPA1 were selectively prevented by disrupting the interaction of the carboxy-lobe of calmodulin with a calmodulin-binding domain in the C-terminus of TRPA1. Calmodulin is thus a critical Ca2+ sensor enabling TRPA1 to respond to diverse Ca2+ signals distinctly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
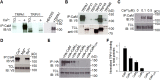

Similar articles
-
Calmodulin binding is required for calcium mediated TRPA1 desensitization.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 12:2024.12.11.627969. doi: 10.1101/2024.12.11.627969. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39713425 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
TRPA1 ion channel stimulation enhances cardiomyocyte contractile function via a CaMKII-dependent pathway.Channels (Austin). 2017 Nov 2;11(6):587-603. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2017.1365206. Epub 2017 Aug 25. Channels (Austin). 2017. PMID: 28792844 Free PMC article.
-
Requirement of extracellular Ca2+ binding to specific amino acids for heat-evoked activation of TRPA1.J Physiol. 2017 Apr 15;595(8):2451-2463. doi: 10.1113/JP274083. Epub 2017 Mar 22. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28194754 Free PMC article.
-
TRPA1.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;222:583-630. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-54215-2_23. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24756722 Review.
-
Calmodulin and CaMKII as molecular switches for cardiac ion channels.Cardiovasc Res. 2007 Mar 1;73(4):641-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.10.019. Epub 2006 Nov 10. Cardiovasc Res. 2007. PMID: 17137569 Review.
Cited by
-
Human Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1 Channel: Structure, Function, and Physiology.Subcell Biochem. 2024;104:207-244. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-58843-3_10. Subcell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38963489 Review.
-
A Novel Discovery: Holistic Efficacy at the Special Organ Level of Pungent Flavored Compounds from Pungent Traditional Chinese Medicine.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 11;20(3):752. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030752. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30754631 Free PMC article.
-
Calmodulin-Dependent Regulation of Overexpressed but Not Endogenous TMEM16A Expressed in Airway Epithelial Cells.Membranes (Basel). 2021 Sep 21;11(9):723. doi: 10.3390/membranes11090723. Membranes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34564540 Free PMC article.
-
Irritant-evoked activation and calcium modulation of the TRPA1 receptor.Nature. 2020 Sep;585(7823):141-145. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2480-9. Epub 2020 Jul 8. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32641835 Free PMC article.
-
Human and Mouse TRPA1 Are Heat and Cold Sensors Differentially Tuned by Voltage.Cells. 2019 Dec 24;9(1):57. doi: 10.3390/cells9010057. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31878344 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zygmunt P. M. & Hogestatt E. D. TRPA1. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 222, 583–630 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Zhang X. Targeting TRP ion channels for itch relief. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 388, 389–399 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Nilius B., Appendino G. & Owsianik G. The transient receptor potential channel TRPA1: from gene to pathophysiology. Pflugers Arch. 464, 425–458 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Julius D. TRP channels and pain. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 29, 355–384 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

