Combined Effects of Curcumin and Lycopene or Bixin in Yoghurt on Inhibition of LDL Oxidation and Increases in HDL and Paraoxonase Levels in Streptozotocin-Diabetic Rats
- PMID: 28333071
- PMCID: PMC5412263
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18040332
Combined Effects of Curcumin and Lycopene or Bixin in Yoghurt on Inhibition of LDL Oxidation and Increases in HDL and Paraoxonase Levels in Streptozotocin-Diabetic Rats
Abstract
Combination therapy using natural antioxidants to manage diabetes mellitus and its complications is an emerging trend. The aim of this study was to investigate the changes promoted by treatment of streptozotocin (STZ)-diabetic rats with yoghurt enriched with the bioactives curcumin, lycopene, or bixin (the latter two being carotenoids). Antioxidants were administered individually, or as mixtures, and biomarkers of metabolic and oxidative disturbances, particularly those associated with cardiovascular risk, were assessed. Treatment of STZ-diabetic rats with natural products individually decreased glycemia, triacylglycerol, total-cholesterol, oxidative stress biomarkers, including oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL), and increased the activities of antioxidant enzymes. Individual carotenoids increased both high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and paraoxonase levels, whereas curcumin increased only paraoxonase. Treatments with mixtures of curcumin and lycopene or bixin had combined effects, decreasing biomarkers of carbohydrate and lipid disturbances (curcumin effect), increasing the HDL levels (carotenoids effects) and mitigating oxidative stress (curcumin and carotenoids effects). The combined effects also led to prevention of the LDL oxidation, thereby mitigating the cardiovascular risk in diabetes. These findings provide evidence for the beneficial effect of curcumin and carotenoid mixtures as a supplementation having antioxidant and antiatherogenic potentials, thus appearing as an interesting strategy to be studied as a complementary therapy for diabetic complications.
Keywords: bixin; cardiovascular risk; curcumin; diabetes mellitus; lycopene; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

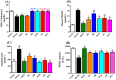
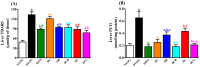
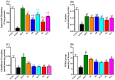
References
-
- Fowler M.J. Microvascular and Macrovascular Complications of Diabetes. Clin. Diabetes. 2008;26:77–82. doi: 10.2337/diaclin.26.2.77. - DOI
-
- International Diabetes Federation IDF Diabetes Atlas, 7th ed. [(accessed on 12 December 2016)]. Available online: http://www.diabetesatlas.org/
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

