Effects of Melatonin on Liver Injuries and Diseases
- PMID: 28333073
- PMCID: PMC5412268
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18040673
Effects of Melatonin on Liver Injuries and Diseases
Abstract
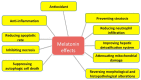
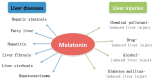
Liver injuries and diseases are serious health problems worldwide. Various factors, such as chemical pollutants, drugs, and alcohol, could induce liver injuries. Liver diseases involve a wide range of liver pathologies, including hepatic steatosis, fatty liver, hepatitis, fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocarcinoma. Despite all the studies performed up to now, therapy choices for liver injuries and diseases are very few. Therefore, the search for a new treatment that could safely and effectively block or reverse liver injuries and diseases remains a priority. Melatonin is a well-known natural antioxidant, and has many bioactivities. There are numerous studies investigating the effects of melatonin on liver injuries and diseases, and melatonin could regulate various molecular pathways, such as inflammation, proliferation, apoptosis, metastasis, and autophagy in different pathophysiological situations. Melatonin could be used for preventing and treating liver injuries and diseases. Herein, we conduct a review summarizing the potential roles of melatonin in liver injuries and diseases, paying special attention to the mechanisms of action.
Keywords: cirrhosis; effect; fatty liver; fibrosis; hepatitis; hepatocarcinoma; liver injuries; melatonin; steatosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical