Genomic landscape of extended-spectrum β-lactamase resistance in Escherichia coli from an urban African setting
- PMID: 28333330
- PMCID: PMC5437524
- DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkx058
Genomic landscape of extended-spectrum β-lactamase resistance in Escherichia coli from an urban African setting
Abstract
Objectives: Efforts to treat Escherichia coli infections are increasingly being compromised by the rapid, global spread of antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Whilst AMR in E. coli has been extensively investigated in resource-rich settings, in sub-Saharan Africa molecular patterns of AMR are not well described. In this study, we have begun to explore the population structure and molecular determinants of AMR amongst E. coli isolates from Malawi.
Methods: Ninety-four E. coli isolates from patients admitted to Queen's Hospital, Malawi, were whole-genome sequenced. The isolates were selected on the basis of diversity of phenotypic resistance profiles and clinical source of isolation (blood, CSF and rectal swab). Sequence data were analysed using comparative genomics and phylogenetics.
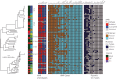
Results: Our results revealed the presence of five clades, which were strongly associated with E. coli phylogroups A, B1, B2, D and F. We identified 43 multilocus STs, of which ST131 (14.9%) and ST12 (9.6%) were the most common. We identified 25 AMR genes. The most common ESBL gene was bla CTX-M-15 and it was present in all five phylogroups and 11 STs, and most commonly detected in ST391 (4/4 isolates), ST648 (3/3 isolates) and ST131 [3/14 (21.4%) isolates].
Conclusions: This study has revealed a high diversity of lineages associated with AMR, including ESBL and fluoroquinolone resistance, in Malawi. The data highlight the value of longitudinal bacteraemia surveillance coupled with detailed molecular epidemiology in all settings, including low-income settings, in describing the global epidemiology of ESBL resistance.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Kotloff KL, Nataro JP, Blackwelder WC. et al. Burden and aetiology of diarrhoeal disease in infants and young children in developing countries (the Global Enteric Multicenter Study, GEMS): a prospective, case-control study. Lancet 2013; 382: 209–22. - PubMed
-
- Liu L, Johnson HL, Cousens S. et al. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality: an updated systematic analysis for 2010 with time trends since 2000. Lancet 2012; 379: 2151–61. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

