Cyclooxygenase-2 Induction by Amino Acid Deprivation Requires p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase in Human Glioma Cells
- PMID: 28333553
- PMCID: PMC6300144
- DOI: 10.1080/07357907.2017.1292517
Cyclooxygenase-2 Induction by Amino Acid Deprivation Requires p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase in Human Glioma Cells
Abstract
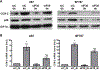
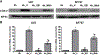
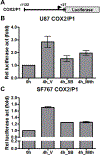
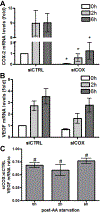
Glioblastomas (GBMs) are malignant brain tumors that can outstrip nutrient supplies due to rapid growth. Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) has been linked to GBMs and may contribute to their aggressive phenotypes. Amino acid starvation results in COX-2 mRNA and protein induction in multiple human glioma cell lines in a process requiring p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38-MAPK) and the Sp1 transcription factor. Increased vascular endothelial growth factor expression results from starvation-dependent COX-2 induction. These data suggest that COX-2 induction with amino acid deprivation may be a part of the adaptation of glioma cells to these conditions, and potentially alter cellular response to anti-neoplastic therapy.
Keywords: COX-2; Glioblastomas; VEGF; amino acid deprivation; p38-MAPK.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

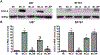


References
-
- Smith WL; DeWitt DL; Garavito RM Cyclooxygenases: structural, cellular, and molecular biology. Annu Rev Biochem 2000. 69, 145–82. - PubMed
-
- Dandekar DS; Lokeshwar BL Inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 expression by Tet-inducible COX-2 antisense cDNA in hormone-refractory prostate cancer significantly slows tumor growth and improves efficacy of chemotherapeutic drugs. Clin Cancer Res 2004. 10, 8037–47. - PubMed
-
- Kishi K; Petersen S; Petersen C; Hunter N; Mason K; Masferrer JL; Tofilon PJ; Milas L Preferential enhancement of tumor radioresponse by a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor. Cancer Res 2000. 60, 1326–31. - PubMed
-
- Oshima M; Dinchuk JE; Kargman SL; Oshima H; Hancock B; Kwong E; Trzaskos JM; Evans JF; Taketo MM Suppression of intestinal polyposis in Apc delta716 knockout mice by inhibition of cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2). Cell 1996. 87, 803–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
