RNAscClust: clustering RNA sequences using structure conservation and graph based motifs
- PMID: 28334186
- PMCID: PMC5870858
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx114
RNAscClust: clustering RNA sequences using structure conservation and graph based motifs
Abstract
Motivation: Clustering RNA sequences with common secondary structure is an essential step towards studying RNA function. Whereas structural RNA alignment strategies typically identify common structure for orthologous structured RNAs, clustering seeks to group paralogous RNAs based on structural similarities. However, existing approaches for clustering paralogous RNAs, do not take the compensatory base pair changes obtained from structure conservation in orthologous sequences into account.
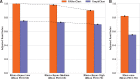
Results: Here, we present RNAscClust , the implementation of a new algorithm to cluster a set of structured RNAs taking their respective structural conservation into account. For a set of multiple structural alignments of RNA sequences, each containing a paralog sequence included in a structural alignment of its orthologs, RNAscClust computes minimum free-energy structures for each sequence using conserved base pairs as prior information for the folding. The paralogs are then clustered using a graph kernel-based strategy, which identifies common structural features. We show that the clustering accuracy clearly benefits from an increasing degree of compensatory base pair changes in the alignments.
Availability and implementation: RNAscClust is available at http://www.bioinf.uni-freiburg.de/Software/RNAscClust .
Contact: gorodkin@rth.dk or backofen@informatik.uni-freiburg.de.
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
© The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures

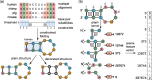
 , the feature is counted twice while the other neighborhood subgraphs are unique. The feature extraction for N-N decorated structures is implemented the same way (Color version of this figure is available at Bioinformatics online.)
, the feature is counted twice while the other neighborhood subgraphs are unique. The feature extraction for N-N decorated structures is implemented the same way (Color version of this figure is available at Bioinformatics online.)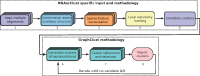
References
-
- Backofen R., Hess W.R. (2010) Computational prediction of sRNAs and their targets in bacteria. RNA Biol., 7, 33–42. - PubMed
-
- Broder A.Z. (1997). On the resemblance and containment of documents. In: Compression and Complexity of Sequences 1997 (Proceedings), pp. 21–29.
-
- Costa F., De Grave K. (2010). Fast neighborhood subgraph pairwise distance kernel. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-10), Haifa, Israel, pp. 255–262. Omnipress.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

