Elongated and Shortened Peptidomimetic Inhibitors of the Proprotein Convertase Furin
- PMID: 28334511
- PMCID: PMC5572662
- DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.201700108
Elongated and Shortened Peptidomimetic Inhibitors of the Proprotein Convertase Furin
Abstract
Novel elongated and shortened derivatives of the peptidomimetic furin inhibitor phenylacetyl-Arg-Val-Arg-4-amidinobenzylamide were synthesized. The most potent compounds, such as Nα (carbamidoyl)Arg-Arg-Val-Arg-4-amidinobenzylamide (Ki =6.2 pm), contain additional basic residues at the N terminus and inhibit furin in the low-picomolar range. Furthermore, to decrease the molecular weight of this inhibitor type, compounds that lack the P5 moiety were prepared. The best inhibitors of this series, 5-(guanidino)valeroyl-Val-Arg-4-amidinobenzylamide and its P3 tert-leucine analogue displayed Ki values of 2.50 and 1.26 nm, respectively. Selected inhibitors, together with our previously described 4-amidinobenzylamide derivatives as references, were tested in cell culture for their activity against furin-dependent infectious pathogens. The propagation of the alphaviruses Semliki Forest virus and chikungunya virus was strongly inhibited in the presence of selected derivatives. Moreover, a significant protective effect of the inhibitors against diphtheria toxin was observed. These results confirm that the inhibition of furin should be a promising approach for the short-term treatment of acute infectious diseases.
Keywords: Semliki Forest virus; alphaviruses; chikungunya virus; diphtheria toxin; furin; inhibitors.
© 2017 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures


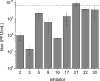

 ), 3 (
), 3 (
 ), 9 (
), 9 (
 ) and 16 (●). Titers were determined by plaque assay at 24 h post-infection. Data represent the mean ± SE for three independent experiments.
) and 16 (●). Titers were determined by plaque assay at 24 h post-infection. Data represent the mean ± SE for three independent experiments.
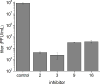
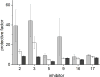
Similar articles
-
Development and Prospects of Furin Inhibitors for Therapeutic Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 24;25(17):9199. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179199. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New substrate analogue furin inhibitors derived from 4-amidinobenzylamide.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011 Aug 15;21(16):4695-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.06.091. Epub 2011 Jun 25. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011. PMID: 21757345
-
Novel Furin Inhibitors with Potent Anti-infectious Activity.ChemMedChem. 2015 Jul;10(7):1218-31. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201500103. Epub 2015 May 14. ChemMedChem. 2015. PMID: 25974265
-
Highly potent inhibitors of proprotein convertase furin as potential drugs for treatment of infectious diseases.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jun 22;287(26):21992-2003. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.332643. Epub 2012 Apr 26. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22539349 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical structure and properties of low-molecular furin inhibitors.Ukr Biochem J. 2016 Nov-Dec;88(6):5-25. doi: 10.15407/ubj88.06.005. Ukr Biochem J. 2016. PMID: 29235831 Review.
Cited by
-
The Proteolytic Regulation of Virus Cell Entry by Furin and Other Proprotein Convertases.Viruses. 2019 Sep 9;11(9):837. doi: 10.3390/v11090837. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31505793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Basicity Makes the Difference: Improved Canavanine-Derived Inhibitors of the Proprotein Convertase Furin.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2021 Feb 9;12(3):426-432. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.0c00651. eCollection 2021 Mar 11. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2021. PMID: 33732412 Free PMC article.
-
The Path to Therapeutic Furin Inhibitors: From Yeast Pheromones to SARS-CoV-2.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 22;23(7):3435. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073435. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35408793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro Evaluation of Antipseudomonal Activity and Safety Profile of Peptidomimetic Furin Inhibitors.Biomedicines. 2024 Sep 11;12(9):2075. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12092075. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39335588 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Prospects of Furin Inhibitors for Therapeutic Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 24;25(17):9199. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179199. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273149 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

