Genetic regulation of gene expression in the epileptic human hippocampus
- PMID: 28334860
- PMCID: PMC5411756
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddx061
Genetic regulation of gene expression in the epileptic human hippocampus
Abstract
Epilepsy is a serious and common neurological disorder. Expression quantitative loci (eQTL) analysis is a vital aid for the identification and interpretation of disease-risk loci. Many eQTLs operate in a tissue- and condition-specific manner. We have performed the first genome-wide cis-eQTL analysis of human hippocampal tissue to include not only normal (n = 22) but also epileptic (n = 22) samples. We demonstrate that disease-associated variants from an epilepsy GWAS meta-analysis and a febrile seizures (FS) GWAS are significantly more enriched with epilepsy-eQTLs than with normal hippocampal eQTLs from two larger independent published studies. In contrast, GWAS meta-analyses of two other brain diseases associated with hippocampal pathology (Alzheimer's disease and schizophrenia) are more enriched with normal hippocampal eQTLs than with epilepsy-eQTLs. These observations suggest that an eQTL analysis that includes disease-affected brain tissue is advantageous for detecting additional risk SNPs for the afflicting and closely related disorders, but not for distinct diseases affecting the same brain regions. We also show that epilepsy eQTLs are enriched within epilepsy-causing genes: an epilepsy cis-gene is significantly more likely to be a causal gene for a Mendelian epilepsy syndrome than to be a causal gene for another Mendelian disorder. Epilepsy cis-genes, compared to normal hippocampal cis-genes, are more enriched within epilepsy-causing genes. Hence, we utilize the epilepsy eQTL data for the functional interpretation of epilepsy disease-risk variants and, thereby, highlight novel potential causal genes for sporadic epilepsy. In conclusion, an epilepsy-eQTL analysis is superior to normal hippocampal tissue eQTL analyses for identifying the variants and genes underlying epilepsy.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
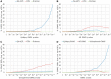
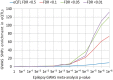
Similar articles
-
Bayesian genome-wide TWAS with reference transcriptomic data of brain and blood tissues identified 141 risk genes for Alzheimer's disease dementia.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024 Jun 1;16(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s13195-024-01488-7. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38824563 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation and cis-regulation of gene expression by prostate cancer risk SNPs.PLoS Genet. 2020 Mar 30;16(3):e1008667. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008667. eCollection 2020 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 32226005 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide mapping of genetic determinants influencing DNA methylation and gene expression in human hippocampus.Nat Commun. 2017 Nov 15;8(1):1511. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01818-4. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 29142228 Free PMC article.
-
Expression Quantitative Trait Loci Information Improves Predictive Modeling of Disease Relevance of Non-Coding Genetic Variation.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 16;10(10):e0140758. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140758. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26474488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain expression quantitative trait locus mapping informs genetic studies of psychiatric diseases.Neurosci Bull. 2011 Apr;27(2):123-33. doi: 10.1007/s12264-011-1203-5. Neurosci Bull. 2011. PMID: 21441974 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Meta-Analysis Identifies Two Novel Risk Loci for Epilepsy.Front Neurosci. 2021 Aug 12;15:722592. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.722592. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34456681 Free PMC article.
-
Guidelines for bioinformatics of single-cell sequencing data analysis in Alzheimer's disease: review, recommendation, implementation and application.Mol Neurodegener. 2022 Mar 2;17(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13024-022-00517-z. Mol Neurodegener. 2022. PMID: 35236372 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of potential crucial genes and therapeutic targets for epilepsy.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Jan 11;29(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01643-8. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38212777 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Set Enrichment Analysis Detected Immune Cell-Related Pathways Associated with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Aug 26;2022:2371347. doi: 10.1155/2022/2371347. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36060137 Free PMC article.
-
CBP Is Required for Establishing Adaptive Gene Programs in the Adult Mouse Brain.J Neurosci. 2022 Oct 19;42(42):7984-8001. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0970-22.2022. Epub 2022 Sep 15. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36109165 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sander J.W. (2003) The natural history of epilepsy in the era of new antiepileptic drugs and surgical treatment. Epilepsia, 44 (Suppl. 1), 17–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

