The primary transcriptome of Neisseria meningitidis and its interaction with the RNA chaperone Hfq
- PMID: 28334889
- PMCID: PMC5449619
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkx168
The primary transcriptome of Neisseria meningitidis and its interaction with the RNA chaperone Hfq
Abstract
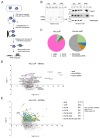
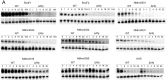
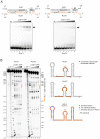
Neisseria meningitidis is a human commensal that can also cause life-threatening meningitis and septicemia. Despite growing evidence for RNA-based regulation in meningococci, their transcriptome structure and output of regulatory small RNAs (sRNAs) are incompletely understood. Using dRNA-seq, we have mapped at single-nucleotide resolution the primary transcriptome of N. meningitidis strain 8013. Annotation of 1625 transcriptional start sites defines transcription units for most protein-coding genes but also reveals a paucity of classical σ70-type promoters, suggesting the existence of activators that compensate for the lack of -35 consensus sequences in N. meningitidis. The transcriptome maps also reveal 65 candidate sRNAs, a third of which were validated by northern blot analysis. Immunoprecipitation with the RNA chaperone Hfq drafts an unexpectedly large post-transcriptional regulatory network in this organism, comprising 23 sRNAs and hundreds of potential mRNA targets. Based on this data, using a newly developed gfp reporter system we validate an Hfq-dependent mRNA repression of the putative colonization factor PrpB by the two trans-acting sRNAs RcoF1/2. Our genome-wide RNA compendium will allow for a better understanding of meningococcal transcriptome organization and riboregulation with implications for colonization of the human nasopharynx.
© The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures





References
-
- Henriques-Normark B., Normark S.. Commensal pathogens, with a focus on Streptococcus pneumoniae, and interactions with the human host. Exp. Cell Res. 2010; 316:1408–1414. - PubMed
-
- Stephens D.S., Greenwood B., Brandtzaeg P.. Epidemic meningitis, meningococcaemia, and Neisseria meningitidis. Lancet. 2007; 369:2196–2210. - PubMed
-
- Greenwood B. Manson lecture. Meningococcal meningitis in africa. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1999; 93:341–353. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

