Association analyses of East Asian individuals and trans-ancestry analyses with European individuals reveal new loci associated with cholesterol and triglyceride levels
- PMID: 28334899
- PMCID: PMC6075203
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddx062
Association analyses of East Asian individuals and trans-ancestry analyses with European individuals reveal new loci associated with cholesterol and triglyceride levels
Erratum in
-
Association analyses of East Asian individuals and trans-ancestry analyses with European individuals reveal new loci associated with cholesterol and triglyceride levels.Hum Mol Genet. 2018 Mar 15;27(6):1122. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx439. Hum Mol Genet. 2018. PMID: 29351605 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
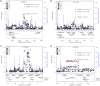
Large-scale meta-analyses of genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified >175 loci associated with fasting cholesterol levels, including total cholesterol (TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and triglycerides (TG). With differences in linkage disequilibrium (LD) structure and allele frequencies between ancestry groups, studies in additional large samples may detect new associations. We conducted staged GWAS meta-analyses in up to 69,414 East Asian individuals from 24 studies with participants from Japan, the Philippines, Korea, China, Singapore, and Taiwan. These meta-analyses identified (P < 5 × 10-8) three novel loci associated with HDL-C near CD163-APOBEC1 (P = 7.4 × 10-9), NCOA2 (P = 1.6 × 10-8), and NID2-PTGDR (P = 4.2 × 10-8), and one novel locus associated with TG near WDR11-FGFR2 (P = 2.7 × 10-10). Conditional analyses identified a second signal near CD163-APOBEC1. We then combined results from the East Asian meta-analysis with association results from up to 187,365 European individuals from the Global Lipids Genetics Consortium in a trans-ancestry meta-analysis. This analysis identified (log10Bayes Factor ≥6.1) eight additional novel lipid loci. Among the twelve total loci identified, the index variants at eight loci have demonstrated at least nominal significance with other metabolic traits in prior studies, and two loci exhibited coincident eQTLs (P < 1 × 10-5) in subcutaneous adipose tissue for BPTF and PDGFC. Taken together, these analyses identified multiple novel lipid loci, providing new potential therapeutic targets.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Wannamethee G., Shaper A.G. (1994) The association between heart rate and blood pressure, blood lipids and other cardiovascular risk factors. J. Cardiovasc. Risk, 1, 223–230. - PubMed
-
- Peloso G.M., Auer P.L., Bis J.C., Voorman A., Morrison A.C., Stitziel N.O., Brody J.A., Khetarpal S.A., Crosby J.R., Fornage M., et al. (2014) Association of low-frequency and rare coding-sequence variants with blood lipids and coronary heart disease in 56,000 whites and blacks. Am. J. Hum. Genet., 94, 223–232. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F31 HL127984/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA122756/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA070867/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA124558/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- D43 TW009077/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA137013/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK078150/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES010126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA082729/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD030880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA144034/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK104371/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA173640/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR020649/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA090899/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 TW005596/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA122364/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL108427/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL098049/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA064277/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY014684/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA148667/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087263/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL072507/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL085144/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL069768/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056350/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R24 HD050924/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL090682/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA182910/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P2C HD050924/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA182876/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

