Vitamin E Nicotinate
- PMID: 28335380
- PMCID: PMC5384183
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox6010020
Vitamin E Nicotinate
Erratum in
-
Correction: Duncan, K.R., Suzuki, Y.J. Vitamin E Nicotinate. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 20.Antioxidants (Basel). 2018 May 3;7(5):64. doi: 10.3390/antiox7050064. Antioxidants (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29751491 Free PMC article.
Abstract
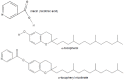
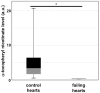
Vitamin E refers to a family of compounds that function as lipid-soluble antioxidants capable of preventing lipid peroxidation. Naturally occurring forms of vitamin E include tocopherols and tocotrienols. Vitamin E in dietary supplements and fortified foods is often an esterified form of α-tocopherol, the most common esters being acetate and succinate. The vitamin E esters are hydrolyzed and converted into free α-tocopherol prior to absorption in the intestinal tract. Because its functions are relevant to many chronic diseases, vitamin E has been extensively studied in respect to a variety of diseases as well as cosmetic applications. The forms of vitamin E most studied are natural α-tocopherol and the esters α-tocopheryl acetate and α-tocopheryl succinate. A small number of studies include or focus on another ester form, α-tocopheryl nicotinate, an ester of vitamin E and niacin. Some of these studies raise the possibility of differences in metabolism and in efficacy between vitamin E nicotinate and other forms of vitamin E. Recently, through metabolomics studies, we identified that α-tocopheryl nicotinate occurs endogenously in the heart and that its level is dramatically decreased in heart failure, indicating the possible biological importance of this vitamin E ester. Since knowledge about vitamin E nicotinate is not readily available in the literature, the purpose of this review is to summarize and evaluate published reports, specifically with respect to α-tocopheryl nicotinate with an emphasis on the differences from natural α-tocopherol or α-tocopheryl acetate.
Keywords: tocopherol nicotinate; tocopheryl nicotinate; vitamin E nicotinate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Brigelius-Flohe R., Traber M.G. Vitamin E: Function and metabolism. FASEB J. 1999;13:1145–1155. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

