Ipsilateral and contralateral sensory changes in healthy subjects after experimentally induced concomitant sensitization and hypoesthesia
- PMID: 28335745
- PMCID: PMC5364678
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-017-0839-9
Ipsilateral and contralateral sensory changes in healthy subjects after experimentally induced concomitant sensitization and hypoesthesia
Abstract
Background: In unilateral neuropathic pain. e.g. after peripheral nerve injury, both positive and negative sensory signs occur often, accompanied by minor but equally directed contralateral sensory changes. To mimic this feature, we experimentally aimed to induce concomitant c-fibre sensitization and block in healthy subjects and analyzed the bilateral sensory changes by quantitative sensory testing (QST) using the protocol of the German Research Network on Neuropathic Pain.
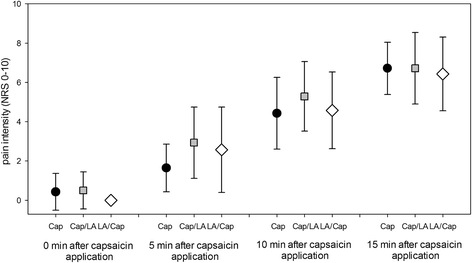
Methods: Twenty eight healthy subjects were firstly randomized in 2 groups to receive either topical capsaicin (0.6%, 12 cm2, application duration: 15 min.) or a lidocaine/prilocaine patch (25/25 mg, 10 cm2, application duration: 60 min.) on the right volar forearm. Secondly, 7-14 days later in the same area either at first capsaicin (for 15 min.) and immediately afterwards local anesthetics (for 60 min.) was applied (Cap/LA), or in inversed order with the same application duration (LA/Cap). Before, after each application and 7-14 days later a QST was performed bilaterally.
Statistics: Wilcoxon-test, ANOVA, p < 0.05.
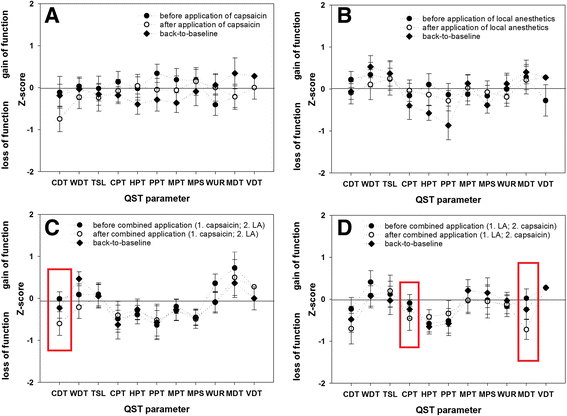
Results: Single application of 0,6% capsaicin induced thermal hypoesthesia, cold hypoalgesia, heat hyperalgesia and tactile allodynia. Lidocaine/prilocaine alone induced thermal and tactile hypoesthesia as well as mechanical and cold hypoalgesia, and a heat hyperalgesia (to a smaller extent). Ipsilaterally both co-applications induced a combination of the above mentioned changes. Significant contralateral sensory changes occurred only after the co-application with concomitant sensitization and hypoesthesia and comprised increased cold (Cap/LA, LA/Cap) and mechanical detection as well as cold pain threshold (LA/Cap).
Conclusion: The present experimental model using combined application of capsaicin and LA imitates partly the complex sensory changes observed in patients with unilateral neuropathic pain and might be used as an additional surrogate model. Only the concomitant use both agents in the same area induces both positive and negative sensory signs ipsilaterally as well as parallel contralateral sensory changes (to a lesser extent).
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT01540877 , registered on 23 February 2012.
Keywords: Capsaicin; Contralateral sensory changes; Experimental pain model; Local anesthetics; Neuropathic pain; Pain mechanisms; Quantitative sensory testing; Sensory profiles; Translational pain research.
Figures


References
-
- Finnerup NB, Attal N, Haroutounian S, McNicol E, Baron R, Dworkin RH, Gilron I, Haanpää M, Hansson P, Jensen TS, Kamerman PR, Lund K, Moore A, Raja SN, Rice AS, Rowbotham M, Sena E, Siddall P, Smith BH, Wallace M. Pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14(2):162–173. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70251-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Demant DT, Lund K, Vollert J, Maier C, Segerdahl M, Finnerup NB, Jensen TS, Sindrup SH. The effect of oxcarbazepine in peripheral neuropathic pain depends on pain phenotype: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phenotype-stratified study. Pain. 2014;155(11):2263–2273. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2014.08.014. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

