Novel compound heterozygous mutations in the OTOF Gene identified by whole-exome sequencing in auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder
- PMID: 28335750
- PMCID: PMC5364697
- DOI: 10.1186/s12881-017-0400-0
Novel compound heterozygous mutations in the OTOF Gene identified by whole-exome sequencing in auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder
Abstract
Background: Many hearing-loss diseases are demonstrated to have Mendelian inheritance caused by mutations in single gene. However, many deaf individuals have diseases that remain genetically unexplained. Auditory neuropathy is a sensorineural deafness in which sounds are able to be transferred into the inner ear normally but the transmission of the signals from inner ear to auditory nerve and brain is injured, also known as auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder (ANSD). The pathogenic mutations of the genes responsible for the Chinese ANSD population remain poorly understood.
Methods: A total of 127 patients with non-syndromic hearing loss (NSHL) were enrolled in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. A hereditary deafness gene mutation screening was performed to identify the mutation sites in four deafness-related genes (GJB2, GJB3, 12S rRNA, and SLC26A4). In addition, whole-exome sequencing (WES) was applied to explore unappreciated mutation sites in the cases with the singularity of its phenotype.
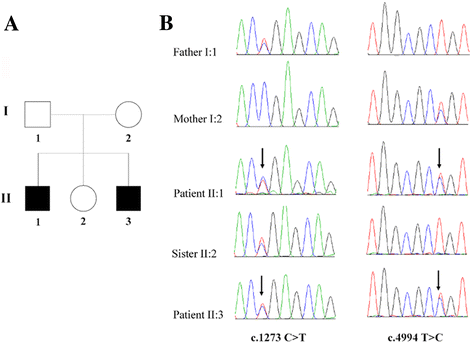
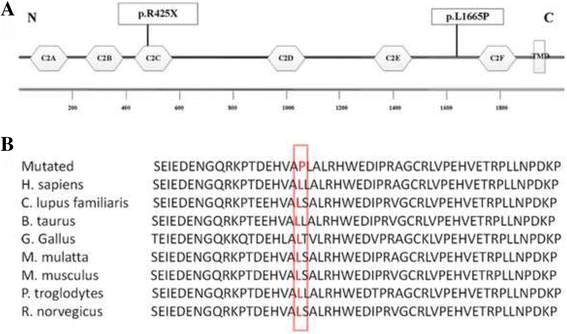
Results: Well-characterized mutations were found in only 8.7% (11/127) of the patients. Interestingly, two mutations in the OTOF gene were identified in two affected siblings with ANSD from a Chinese family, including one nonsense mutation c.1273C > T (p.R425X) and one missense mutation c.4994 T > C (p.L1665P). Furthermore, we employed Sanger sequencing to confirm the mutations in each subject. Two compound heterozygous mutations in the OTOF gene were observed in the two affected siblings, whereas the two parents and unaffected sister were heterozygous carriers of c.1273C > T (father and sister) and c.4994 T > C (mother). The nonsense mutation p.R425X, contributes to a premature stop codon, may result in a truncated polypeptide, which strongly suggests its pathogenicity for ANSD. The missense mutation p.L1665P results in a single amino acid substitution in a highly conserved region.
Conclusions: Two mutations in the OTOF gene in the Chinese deaf population were recognized for the first time. These findings not only extend the OTOF gene mutation spectrum for ANSD but also indicate that whole-exome sequencing is an effective approach to clarify the genetic characteristics in non-syndromic ANSD patients.
Keywords: Auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder; Heterozygous mutations; OTOF gene; Whole-exome sequencing.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder due to Two Novel Compound Heterozygous OTOF Mutations in Two Chinese Families.Neural Plast. 2019 Nov 18;2019:9765276. doi: 10.1155/2019/9765276. eCollection 2019. Neural Plast. 2019. PMID: 31827501 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic analysis of auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder in the Korean population.Gene. 2013 Jun 10;522(1):65-9. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.02.057. Epub 2013 Apr 4. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23562982
-
Variants of OTOF and PJVK genes in Chinese patients with auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24000. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024000. Epub 2011 Sep 15. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21935370 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted next generation sequencing reveals OTOF mutations in auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2018 Dec;115:19-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2018.09.008. Epub 2018 Sep 14. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2018. PMID: 30368385 Review.
-
Mutation spectrum of non-syndromic hearing loss in the UAE, a retrospective cohort study and literature review.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2022 Nov;10(11):e2052. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.2052. Epub 2022 Sep 2. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2022. PMID: 36056583 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of novel variants in MYO15A, OTOF, and RDX with hearing loss by next-generation sequencing.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019 Aug;7(8):e808. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.808. Epub 2019 Jun 28. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019. PMID: 31250571 Free PMC article.
-
[The natural history of the relationship between OTOF mutation-related genotypes and audiological phenotypes].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025 Apr;39(4):379-385. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2025.04.016. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40166883 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Comprehensive functional network analysis and screening of deleterious pathogenic variants in non-syndromic hearing loss causative genes.Biosci Rep. 2021 Oct 29;41(10):BSR20211865. doi: 10.1042/BSR20211865. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34714320 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic analysis of 106 sporadic cases with hearing loss in the UAE population.Hum Genomics. 2024 Jun 7;18(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s40246-024-00630-8. Hum Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38844983 Free PMC article.
-
The natural history, clinical outcomes, and genotype-phenotype relationship of otoferlin-related hearing loss: a systematic, quantitative literature review.Hum Genet. 2023 Oct;142(10):1429-1449. doi: 10.1007/s00439-023-02595-5. Epub 2023 Sep 7. Hum Genet. 2023. PMID: 37679651 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

