Sophorae Flos extract inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation by suppressing the NF-κB/NFATc1 pathway in mouse bone marrow cells
- PMID: 28335757
- PMCID: PMC5364702
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-016-1550-x
Sophorae Flos extract inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation by suppressing the NF-κB/NFATc1 pathway in mouse bone marrow cells
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: Sophorae Flos extract inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation by suppressing the NF-κB/NFATc1 pathway in mouse bone marrow cells.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Apr 28;17(1):235. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1745-9. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28454536 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Sophorae Flos (SF) is a composite of flowers and buds of Styphnolobium japonicum (L.) Schott and has been used in traditional Korean and Chinese medicine for the treatment of hemostasis and inflammation. Previous studies reported that SF possesses anti-obesity properties, as well as anti-allergic, anti-proliferative, and anti-inflammatory activities. However, the effect of SF in bone resorption has not been studies. In this study, we examined the potential of SF extract (SFE) to inhibit receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL) -induced osteoclast differentiation in cultured mouse-derived bone marrow macrophages (BMMs).
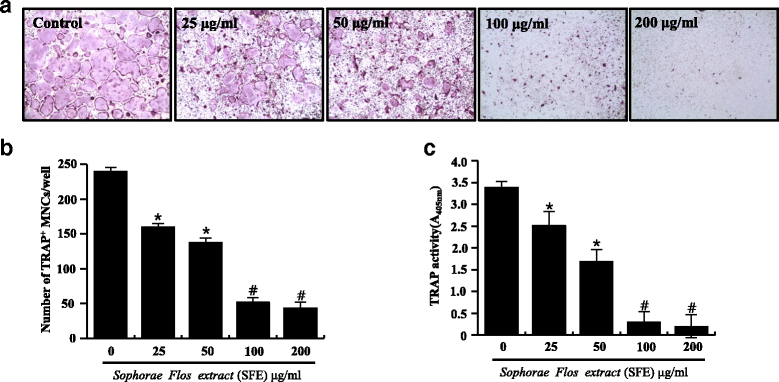
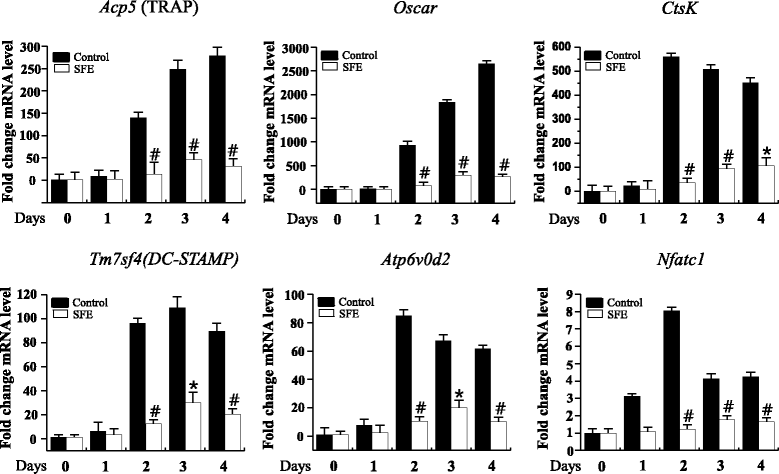
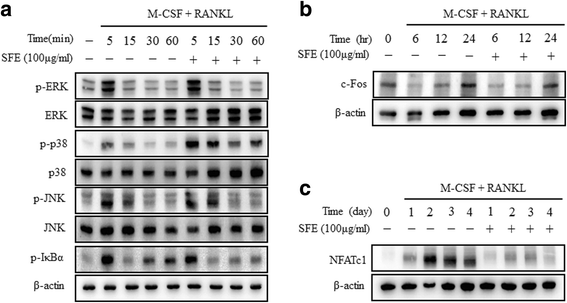
Methods: BMMs, that act as osteoclast precursors, were cultured with M-CSF (50 ng/ml) and RANKL (100 ng/ml) for 4 days to generate osteoclasts. Osteoclast differentiation was measured by tartrate-resistant acidic phosphatase (TRAP) staining and the TRAP solution assay. Osteoclast differentiation marker genes were analyzed by the quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis. RANKLs signaling pathways were confirmed through western blotting.
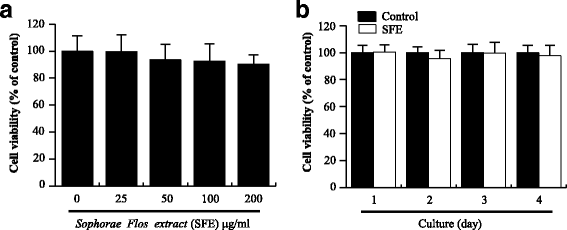
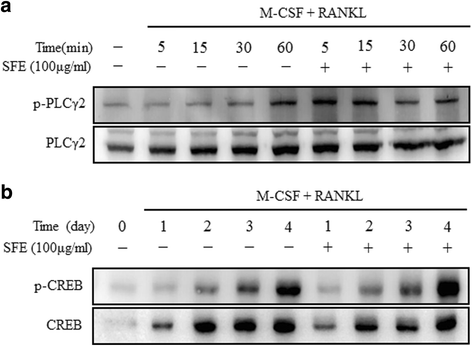
Results: SFE significantly decreased osteoclast differentiation in a dose-dependent manner. SFE inhibited RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by suppressing NF-κB activation. By contrast, SFE did not affect phospholipase C gamma 2 or subsequent cAMP response element binding activation. SFE inhibited the RANKL-induced expression of nuclear factor of activated T cells c1 (NFATc1).
Conclusions: SFE attenuated the RANKL-mediated induction of NF-κB through inhibition of IκBα phosphorylation, which contributed to inhibiting of RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation through downregulation of NFATc1.
Keywords: NF-κB; NFATc1; Osteoclast; PLCγ2; Sophorae Flos (SF).
Figures
References
-
- Kong YY, Yoshida H, Sarosi I, Tan HL, Timms E, Capparelli C, Morony S, Oliveira-dos-Santos AJ, Van G, Itie A, Khoo W, Wakeham A, Dunstan CR, Lacey DL, Mak TW, Boyle WJ, Penninger JM. OPGL is a key regulator of osteoclastogenesis, lymphocyte development and lymph-node organogenesis. Nature. 1999;397:315–23. doi: 10.1038/16852. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

