pTAC10, a Key Subunit of Plastid-Encoded RNA Polymerase, Promotes Chloroplast Development
- PMID: 28336770
- PMCID: PMC5411158
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.17.00248
pTAC10, a Key Subunit of Plastid-Encoded RNA Polymerase, Promotes Chloroplast Development
Abstract
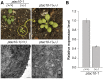
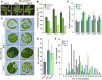
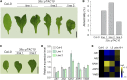
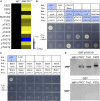
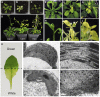
Regulation of photosynthetic gene expression by plastid-encoded RNA polymerase (PEP) is essential for chloroplast development. The activity of PEP largely relies on at least 12 PEP-associated proteins (PAPs) encoded in the nuclear genome of plant cells. A recent model proposed that these PAPs regulate the establishment of the PEP complex through broad PAP-PEP or PAP-PAP interactions. In this study, we identified the Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) seedling-lethal mutant ptac10-1, which has defects in chloroplast development, and found that the mutant phenotype is caused by the suppression of PLASTID S1 RNA-BINDING DOMAIN PROTEIN (pTAC10/PAP3). Analysis of the heterozygous mutant and pTAC10-overexpressing transgenic plants indicated that the expression level of pTAC10 is tightly linked to chloroplast development. Characterization of the interaction of pTAC10 with PAPs revealed that pTAC10 interacts with other PAPs, such as FSD2, FSD3, TrxZ, pTAC7, and pTAC14, but it does not interact with PEP core enzymes, such as rpoA and rpoB. Analysis of pTAC10 interactions using truncated pTAC10 proteins showed that the pTAC10 carboxyl-terminal region downstream of the S1 domain is involved in the pTAC10-PAP interaction. Furthermore, overexpression of truncated pTAC10s lacking the C-terminal regions downstream of the S1 domain could not rescue the ptac10-1 mutant phenotype and induced an abnormal whitening phenotype in Columbia-0 plants. Our observations suggested that these pTAC10-PAP interactions are essential for the formation of the PEP complex and chloroplast development.
© 2017 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Arsova B, Hoja U, Wimmelbacher M, Greiner E, Ustün S, Melzer M, Petersen K, Lein W, Börnke F (2010) Plastidial thioredoxin z interacts with two fructokinase-like proteins in a thiol-dependent manner: evidence for an essential role in chloroplast development in Arabidopsis and Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Cell 22: 1498–1515 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Biswal B, Krupinska K, Biswal UC (2013) Plastid Development in Leaves during Growth and Senescence. Springer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands
-
- Buchanan BB, Gruissem W, Jones RL (2015) Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Plants. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, New Jersey
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

