TGF-β1 stimulates HDAC4 nucleus-to-cytoplasm translocation and NADPH oxidase 4-derived reactive oxygen species in normal human lung fibroblasts
- PMID: 28336812
- PMCID: PMC5495947
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00256.2016
TGF-β1 stimulates HDAC4 nucleus-to-cytoplasm translocation and NADPH oxidase 4-derived reactive oxygen species in normal human lung fibroblasts
Abstract
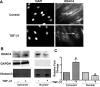
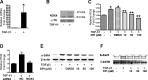
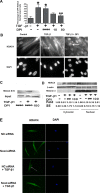
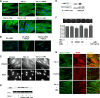
Myofibroblasts are important mediators of fibrogenesis; thus blocking fibroblast-to-myofibroblast differentiation (FMD) may be an effective strategy to treat pulmonary fibrosis (PF). Previously, we reported that histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4) activity is necessary for transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1)-induced human lung FMD. Here, we show that TGF-β1 increases NADPH oxidase 4 (NOX4) mRNA and protein expression in normal human lung fibroblasts (NHLFs) and causes nuclear export of HDAC4. Application of the NOX family inhibitor diphenyleneiodonium chloride reduces TGF-β1-induced HDAC4 nuclear export, expression of the myofibroblast marker α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), and α-SMA fiber formation. Inhibition of HDAC4 nucleus-to-cytoplasm translocation using leptomycin B (LMB) had little effect on α-SMA expression but blocked α-SMA fiber formation. A coimmunoprecipitation assay showed that HDAC4 associates with α-SMA. Moreover, LMB abolishes TGF-β1-induced α-SMA fiber formation and cell contraction. Relevant to human pulmonary fibrosis, idiopathic PF specimens showed significantly higher NOX4 RNA expression and scant HDAC4 staining within nuclei of fibroblast foci myofibroblasts. Taken together, these results indicate that reactive oxygen species promote TGF-β1-mediated myofibroblast differentiation and HDAC4 nuclear export. The physical association of HDAC4 with α-SMA suggests that HDAC4 has a role in regulating the α-SMA cytoskeleton arrangement.
Keywords: HDAC4; IPF; NOX4; myofibroblasts; reactive oxygen species; α-smooth muscle actin.
Copyright © 2017 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Bottomley MJ, Lo Surdo P, Di Giovine P, Cirillo A, Scarpelli R, Ferrigno F, Jones P, Neddermann P, De Francesco R, Steinkühler C, Gallinari P, Carfí A. Structural and functional analysis of the human HDAC4 catalytic domain reveals a regulatory structural zinc-binding domain. J Biol Chem 283: 26694–26704, 2008. doi:10.1074/jbc.M803514200. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

