Nanoemulsified D-Limonene Reduces the Heat Resistance of Salmonella Senftenberg over 50 Times
- PMID: 28336899
- PMCID: PMC5388167
- DOI: 10.3390/nano7030065
Nanoemulsified D-Limonene Reduces the Heat Resistance of Salmonella Senftenberg over 50 Times
Abstract
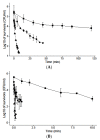
Salmonella Senftenberg is a pathogen agent causative of foodborne disease and it is considered the most heat-resistant serovar within this genus. Food industries use heat treatment and chemical antimicrobials in order to eliminate this microorganism in food, but consumers prefer natural antimicrobials as essential oils and their components. This study evaluates the combined effect of thermal treatments and different concentrations of D-limonene nanoemulsion on the inactivation of Salmonella (S.) Senftenberg. The results showed an important effect of the nanoemulsified D-limonene on the heat resistance of S. Senftenberg. The δ50 °C value was reduced by 85%, 96% and 98% when 0.1, 0.5 and 1 mM of nanoemulsified D-limonene was added to the heating medium. The effect was kept along all the heating temperatures researched and the shape of the survival curves did not change with the addition of the antimicrobial. The results obtained in this research could be very useful for food industries for optimizing or improving heat treatments applied to food.
Keywords: D-limonene; Salmonella Senftenberg; antimicrobial; combined effect; food; heat resistance; nanoemulsions; nanomaterials; safety.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Kumar A., Kumar S. Survival kinetics of Salmonella enterica serotype senftenberg (S. senftenberg) after heat and acid stress. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003;19:985–987. doi: 10.1023/B:WIBI.0000007417.14213.79. - DOI
-
- Mañas P., Pagán R., Álvarez I., Condón S. Survival of Salmonella Senftenberg 775 W to current whole egg pasteurization treatments. Food Microbiol. 2003;20:593–600. doi: 10.1016/S0740-0020(02)00088-6. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources