Fgf21 regulates T-cell development in the neonatal and juvenile thymus
- PMID: 28336912
- PMCID: PMC5428243
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-00349-8
Fgf21 regulates T-cell development in the neonatal and juvenile thymus
Abstract
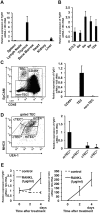
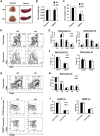
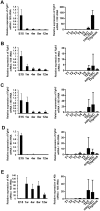
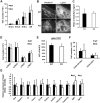
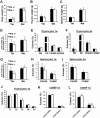
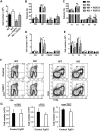
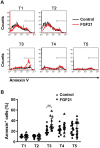
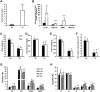
We have previously shown that Fibroblast growth factor 21 (Fgf21) is expressed in the thymus as well as in the liver. In line with this expression profile, Fgf21 was recently reported to protect against ageing-related thymic senescence by improving the function of thymic epithelial cells (TECs). However, the function of Fgf21 in the juvenile thymus remained to be elucidated. We investigated the physiological roles of Fgf21 in the juvenile thymus and found that young Fgf21 knockout mice, but not β-Klotho knockout mice nor adult Fgf21 knockout mice, showed a significant reduction in the percentage of single-positive CD4+ and CD8+ thymocytes without obvious alteration in TECs. Furthermore, treatment with recombinant FGF21 protein rescued the impairment in fetal thymus organ culture (FTOC) of Fgf21 knockout mice. Annexin V staining revealed FGF21 protein enhanced apoptosis of immature thymocytes undergoing selection process in FTOC, suggesting that FGF21 may facilitate the selection of developing T cells. Endocrine Fgf21 from the liver induced by metabolic stimulation did not affect juvenile thymocyte development. Our data suggest that Fgf21 acts as one of intrathymic cytokines in the neonatal and juvenile thymus, involving thymocyte development in a β-Klotho-independent manner.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

