Effect of prolyl hydroxylase domain 2 haplodeficiency on liver progenitor cell characteristics in early mouse hepatocarcinogenesis
- PMID: 28337100
- PMCID: PMC5318796
- DOI: 10.17179/excli2016-607
Effect of prolyl hydroxylase domain 2 haplodeficiency on liver progenitor cell characteristics in early mouse hepatocarcinogenesis
Abstract
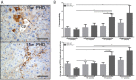
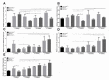
Activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) induces therapy resistant tumours, characterized by increased liver progenitor cell (LPCs) characteristics and poor prognosis. We previously reported corresponding results in mice with HCC in which hypoxia was mimicked by prolyl hydroxylase domain (PHD) inhibition. Here, we aimed at investigating whether induction of LPC characteristics occurs during the onset of hepatocarcinogenesis and if this is associated with activation of Notch signalling. Dietheylnitrosamine (DEN) was used to induce hepatic tumours in PHD2 haplodeficient (PHD2+/-) mice which were euthanized at 5, 10, 15 and 17 weeks following DEN during neoplastic transformation, before tumour formation. Neoplasia and mRNA expression of LPC and Notch markers were evaluated by histology and qPCR on isolated livers. PHD2 haplodeficiency resulted in enhanced expression of HIF target genes after 17 weeks of DEN compared to wild type (WT) littermates but had no effect on the onset of neoplastic transformation. The mRNA expression of Afp and Epcam was increased at all time points following DEN whereas CK19, Prom1 and Notch3 were increased after 17 weeks of DEN, without difference between PHD2+/- and WT mice. MDR1 mRNA expression was increased in all DEN treated mice compared to saline control with increased expression in PHD2+/- compared to WT from 15 weeks. These results indicate that the effects of PHD2 haplodeficiency on the expression of LPC and Notch markers manifest during tumour nodule formation and not early on during neoplastic transformation.
Keywords: diethylnitrosamine; hepatocarcinogenesis; hypoxia; liver progenitor cells; notch; prolyl hydroxylase domain.
Figures


References
-
- Chan AW, Tong JH, Chan SL, Lai PB, To KF. Expression of stemness markers (CD133 and EpCAM) in prognostication of hepatocellular carcinoma. Histopathology. 2014;64:935–950. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
