Dioscin Protects ANIT-Induced Intrahepatic Cholestasis Through Regulating Transporters, Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress
- PMID: 28337145
- PMCID: PMC5340742
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00116
Dioscin Protects ANIT-Induced Intrahepatic Cholestasis Through Regulating Transporters, Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress
Abstract
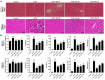
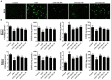
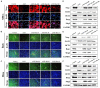
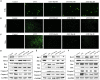
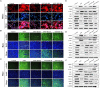
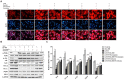
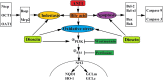
Intrahepatic cholestasis, a clinical syndrome, is caused by excessive accumulation of bile acids in body and liver. Proper regulation of bile acids in liver cells is critical for liver injury. We previously reported the effects of dioscin against α-naphthylisothio- cyanate (ANIT)-induced cholestasis in rats. However, the pharmacological and mechanism data are limited. In our work, the animals of rats and mice, and Sandwich-cultured hepatocytes (SCHs) were caused by ANIT, and dioscin was used for the treatment. The results showed that dioscin markedly altered relative liver weights, restored ALT, AST, ALP, TBIL, GSH, GSH-Px, MDA, SOD levels, and rehabilitated ROS level and cell apoptosis. In mechanism study, dioscin not only significantly regulated the protein levels of Ntcp, OAT1, OCT1, Bsep and Mrp2 to accelerate bile acids excretion, but also regulated the expression levels of Bak, Bcl-xl, Bcl-2, Bax, Caspase 3 and Caspase 9 in vivo and in vitro to improve apoptosis. In addition, dioscin markedly inhibited PI3K/Akt pathway and up-regulated the levels of Nrf2, GCLc, GCLm, NQO1 and HO-1 against oxidative stress (OS) caused by bile acids. These results were further validated by inhibition of PI3K and Akt using the inhibitors of wortmannin and perifosine in SCHs. Our data showed that dioscin had good action against ANIT-caused intrahepatic cholestasis through regulating transporters, apoptosis and OS. This natural product can be considered as one active compound to treat intrahepatic cholestasis in the future.
Keywords: PI3K/Akt pathway; cholestasis; dioscin; oxidative stress; α-naphthylisothiocyanate.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

