Role of Notch signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 28337369
- PMCID: PMC5336494
Role of Notch signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer
Abstract
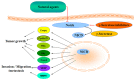
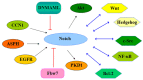
Pancreatic cancer (PC) is one of the highly aggressive malignancies in the United States. It has been shown that multiple signaling pathways are involved in the pathogenesis of PC, such as JNK, PI3K/AKT, Rho GTPase, Hedgehog (Hh) and Skp2. In recent years, accumulated evidence has demonstrated that Notch signaling pathway plays critical roles in the development and progression of PC. Therefore, in this review we discuss the recent literature regarding the function and regulation of Notch in the pathogenesis of PC. Moreover, we describe that Notch signaling pathway could be down-regulated by its inhibitors or natural compounds, which could be a novel approach for the treatment of PC patients.
Keywords: Pancreatic cancer; cellular signaling; notch; target; therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Notch Signaling and Leptin-Notch Crosstalk in Pancreatic Cancer.Medicines (Basel). 2018 Jul 2;5(3):68. doi: 10.3390/medicines5030068. Medicines (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30004402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting notch to eradicate pancreatic cancer stem cells for cancer therapy.Anticancer Res. 2011 Apr;31(4):1105-13. Anticancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21508353 Review.
-
Crosstalk between hedgehog and other signaling pathways as a basis for combination therapies in cancer.Cancer Treat Rev. 2014 Jul;40(6):750-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2014.02.003. Epub 2014 Feb 24. Cancer Treat Rev. 2014. PMID: 24613036 Review.
-
Skp2 is a promising therapeutic target in breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2012 Jan 4;1(57):57. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2011.00057. Front Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22279619 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin-Notch signaling axis is involved in pancreatic cancer progression.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 31;8(5):7740-7752. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13946. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27999190 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Oncolytic viral therapy as a novel potential solution for treatment of pancreatic cancer.Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2025;18(1):53-69. doi: 10.22037/ghfbb.v18i1.3066. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2025. PMID: 40734810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In silico identification and biological evaluation of a selective MAP4K4 inhibitor against pancreatic cancer.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023 Dec;38(1):2166039. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2023.2166039. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36683274 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA FAM83H-AS1 is associated with the prognosis of colorectal carcinoma and promotes cell proliferation by targeting the Notch signaling pathway.Oncol Lett. 2018 Feb;15(2):1861-1868. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.7520. Epub 2017 Dec 5. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29434883 Free PMC article.
-
Study Deciphering the Crucial Involvement of Notch Signaling Pathway in Human Cancers.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024;24(11):1241-1253. doi: 10.2174/0118715303261691231107113548. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 37997805 Review.
-
Complementary effects of Orthosiphon stamineus standardized ethanolic extract and rosmarinic acid in combination with gemcitabine on pancreatic cancer.Biomed J. 2021 Dec;44(6):694-708. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2020.05.015. Epub 2020 May 28. Biomed J. 2021. PMID: 35166208 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–32. - PubMed
-
- Werner J, Combs SE, Springfeld C, Hartwig W, Hackert T, Buchler MW. Advanced-stage pancreatic cancer: therapy options. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013;10:323–333. - PubMed
-
- Hackert T, Buchler MW. Pancreatic cancer: advances in treatment, results and limitations. Dig Dis. 2013;31:51–56. - PubMed
-
- Hidalgo M. Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1605–1617. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
