The RS504393 Influences the Level of Nociceptive Factors and Enhances Opioid Analgesic Potency in Neuropathic Rats
- PMID: 28337574
- PMCID: PMC5527054
- DOI: 10.1007/s11481-017-9729-6
The RS504393 Influences the Level of Nociceptive Factors and Enhances Opioid Analgesic Potency in Neuropathic Rats
Abstract
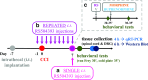
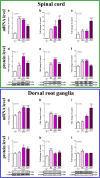
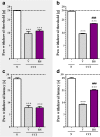
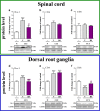
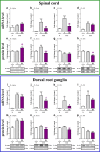
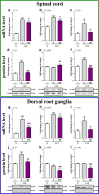
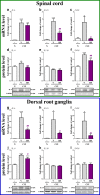
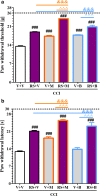
Increasing evidence has indicated that activated glial cells releasing nociceptive factors, such as interleukins and chemokines, are of key importance for neuropathic pain. Significant changes in the production of nociceptive factors are associated with the low effectiveness of opioids in neuropathic pain. Recently, it has been suggested that CCL2/CCR2 signaling is important for nociception. Here, we studied the time course changes in the mRNA/protein level of CD40/Iba-1, CCL2 and CCR2 in the spinal cord/dorsal root ganglia (DRG) in rats following chronic constriction injury (CCI) of the sciatic nerve. Moreover, we examined the influence of intrathecal preemptive and repeated (daily for 7 days) administration of RS504393, CCR2 antagonist, on pain-related behavior and the associated biochemical changes of some nociceptive factors as well as its influence on opioid effectiveness. We observed simultaneous upregulation of Iba-1, CCL2, CCR2 in the spinal cord on 7th day after CCI. Additionally, we demonstrated that repeated administration of RS504393 not only attenuated tactile/thermal hypersensitivity but also enhanced the analgesic properties of morphine and buprenorphine under neuropathy. Our results proof that repeated administration of RS504393 reduced the mRNA and/or protein levels of pronociceptive factors, such as IL-1beta, IL-18, IL-6 and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and some of their receptors in the spinal cord and/or DRG. Furthermore, RS504393 elevated the spinal protein level of antinociceptive IL-1alpha and IL-18 binding protein. Our data provide new evidence that CCR2 is a promising target for diminishing neuropathic pain and enhancing the opioid analgesic effects.
Keywords: Buprenorphine; CCR2; Interleukins; Morphine; RS504393.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding
This study was funded by grants HARMONIA 5 2013/10/M/NZ4/00261 and OPUS 11 2016/21/B/NZ4/00128 National Science Centre, Poland and statutory funds of the Institute of Pharmacology Polish Academy of Sciences.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All applicable international, national, and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the International Association for the Study of Pain and the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory and approved by the II Local Bioethics Committee branch of the National Ethics Committee for Experiments on Animals based at the Institute of Pharmacology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Krakow, Poland.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

