The miR-24-3p/p130Cas: a novel axis regulating the migration and invasion of cancer cells
- PMID: 28337997
- PMCID: PMC5364481
- DOI: 10.1038/srep44847
The miR-24-3p/p130Cas: a novel axis regulating the migration and invasion of cancer cells
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: The miR-24-3p/p130Cas: a novel axis regulating the migration and invasion of cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2021 May 26;11(1):11395. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90393-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34040050 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
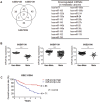
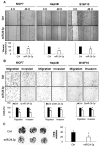
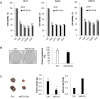
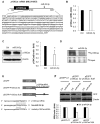
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that negatively regulate gene expression by suppressing translation or facilitating mRNA decay. Differential expression of miRNAs is involved in the pathogenesis of several diseases including cancer. Here, we investigated the role of-miR-24-3p as a downregulated miRNA in metastatic cancer. miR-24-3p was decreased in metastatic cancer and lower expression of miR-24-3p was related to poor survival of cancer patients. Consistently, ectopic expression of miR-24-3p suppressed the cell migration, invasion, and proliferation of MCF7, Hep3B, B16F10, SK-Hep1, and PC-3 cells by directly targeting p130Cas. Stable expression of p130Cas restored miR-24-3p-mediated inhibition of cell migration and invasion. These results suggest that miR-24-3p functions as a tumor suppressor and the miR-24-3p/p130Cas axis is a novel factor of cancer progression by regulating cell migration and invasion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Bartel D. P. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116, 281–297 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

