EGFR Family Members' Regulation of Autophagy Is at a Crossroads of Cell Survival and Death in Cancer
- PMID: 28338617
- PMCID: PMC5406702
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers9040027
EGFR Family Members' Regulation of Autophagy Is at a Crossroads of Cell Survival and Death in Cancer
Abstract
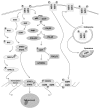
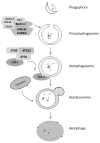
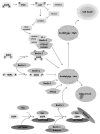
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling pathways are altered in many cancers contributing to increased cell survival. These alterations are caused mainly through increased expression or mutation of EGFR family members EGFR, ErbB2, ErbB3, and ErbB4. These receptors have been successfully targeted for cancer therapy. Specifically, a monoclonal antibody against ErbB2, trastuzumab, and a tyrosine kinase inhibitor against EGFR, gefitinib, have improved the survival of breast and lung cancer patients. Unfortunately, cancer patients frequently become resistant to these inhibitors. This has led to investigating how EGFR can contribute to cell survival and how cancer cells can overcome inhibition of its signaling. Indeed, it is coming into focus that EGFR signaling goes beyond a single signal triggering cell proliferation and survival and is a sensor that regulates the cell's response to microenvironmental stresses such as hypoxia. It acts as a switch that modulates the ability of cancer cells to survive. Autophagy is a process of self-digestion that is inhibited by EGFR allowing cancer cells to survive under stresses that would normally cause death and become resistant to chemotherapy. Inhibiting EGFR signaling allows autophagy to contribute to cell death. This gives new opportunities to develop novel therapeutic strategies to treat cancers that rely on EGFR signaling networks and autophagy. In this review, we summarize the current understanding of EGFR family member regulation of autophagy in cancer cells and how new therapeutic strategies could be developed to overcome drug resistance.
Keywords: autophagy; beclin-1; epidermal growth factor; mitochondria; signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

