A Formaldehyde Sensor Based on Molecularly-Imprinted Polymer on a TiO₂ Nanotube Array
- PMID: 28338635
- PMCID: PMC5419788
- DOI: 10.3390/s17040675
A Formaldehyde Sensor Based on Molecularly-Imprinted Polymer on a TiO₂ Nanotube Array
Abstract
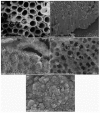
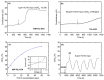
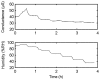
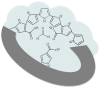
Today, significant attention has been brought to the development of sensitive, specific, cheap, and reliable sensors for real-time monitoring. Molecular imprinting technology is a versatile and promising technology for practical applications in many areas, particularly chemical sensors. Here, we present a chemical sensor for detecting formaldehyde, a toxic common indoor pollutant gas. Polypyrrole-based molecularly-imprinted polymer (PPy-based MIP) is employed as the sensing recognition layer and synthesized on a titanium dioxide nanotube array (TiO₂-NTA) for increasing its surface-to-volume ratio, thereby improving the sensor performance. Our sensor selectively detects formaldehyde in the parts per million (ppm) range at room temperature. It also shows a long-term stability and small fluctuation to humidity variations. These are attributed to the thin fishnet-like structure of the PPy-based MIP on the highly-ordered and vertically-aligned TiO₂-NTA.
Keywords: formaldehyde sensor; humidity influence; molecularly-imprinted polypyrrole; titanium dioxide nanotube array.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures






References
-
- Lee S.-C., Guo H., Li W.-M., Chan L.-Y. Inter-comparison of air pollutant concentrations in different indoor environments in Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 2002;36:1929–1940. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(02)00176-0. - DOI
-
- Van Leeuwen F.X.R., Krzyzanowski M. Air Quality Guidelines. 2nd ed. WHO Regional Office for Europe; Copenhagen, Denmark: 2001.
-
- Occupational Safety and Health Guideline for Formaldehyde Potential Human Carcinogen. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Washington, DC, USA: 1988. [(accessed on 22 March 2017)]. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/docs/81-123/pdfs/0293.pdf.
-
- Yasri N.G., Seddik H., Mosallb M.A. Spectrophotometric Determination of Formaldehyde Based on the Telomerization Reaction of Tryptamine. Arab. J. Chem. 2015;8:487–494. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2011.02.005. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

