Genome-Wide Estimates of Transposable Element Insertion and Deletion Rates in Drosophila Melanogaster
- PMID: 28338986
- PMCID: PMC5447328
- DOI: 10.1093/gbe/evx050
Genome-Wide Estimates of Transposable Element Insertion and Deletion Rates in Drosophila Melanogaster
Abstract
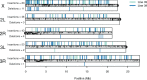
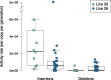
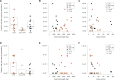
Knowing the rate at which transposable elements (TEs) insert and delete is critical for understanding their role in genome evolution. We estimated spontaneous rates of insertion and deletion for all known, active TE superfamilies present in a set of Drosophila melanogaster mutation-accumulation (MA) lines using whole genome sequence data. Our results demonstrate that TE insertions far outpace TE deletions in D. melanogaster. We found a significant effect of background genotype on TE activity, with higher rates of insertions in one MA line. We also found significant rate heterogeneity between the chromosomes, with both insertion and deletion rates elevated on the X relative to the autosomes. Further, we identified significant associations between TE activity and chromatin state, and tested for associations between TE activity and other features of the local genomic environment such as TE content, exon content, GC content, and recombination rate. Our results provide the most detailed assessment of TE mobility in any organism to date, and provide a useful benchmark for both addressing theoretical predictions of TE dynamics and for exploring large-scale patterns of TE movement in D. melanogaster and other species.
Keywords: Drosophila melanogaster; deletion rate; insertion rate; transposable elements; transposition.
© The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Molecular Biology and Evolution.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sequencing of pooled DNA samples (Pool-Seq) uncovers complex dynamics of transposable element insertions in Drosophila melanogaster.PLoS Genet. 2012 Jan;8(1):e1002487. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002487. Epub 2012 Jan 26. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 22291611 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term evolution of the roo transposable element copy number in mutation accumulation lines of Drosophila melanogaster.Genet Res (Camb). 2011 Jun;93(3):181-7. doi: 10.1017/S0016672311000103. Epub 2011 May 6. Genet Res (Camb). 2011. PMID: 21554776
-
Recurrent insertion and duplication generate networks of transposable element sequences in the Drosophila melanogaster genome.Genome Biol. 2006;7(11):R112. doi: 10.1186/gb-2006-7-11-r112. Genome Biol. 2006. PMID: 17134480 Free PMC article.
-
Maintenance of transposable element copy number in natural populations of Drosophila melanogaster and D. simulans.Genetica. 1997;100(1-3):161-6. Genetica. 1997. PMID: 9440269 Review.
-
What makes transposable elements move in the Drosophila genome?Heredity (Edinb). 2012 May;108(5):461-8. doi: 10.1038/hdy.2011.89. Epub 2011 Oct 5. Heredity (Edinb). 2012. PMID: 21971178 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Asexual Experimental Evolution of Yeast Does Not Curtail Transposable Elements.Mol Biol Evol. 2021 Jun 25;38(7):2831-2842. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab073. Mol Biol Evol. 2021. PMID: 33720342 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Effect of High-Energy Heavy Ion Beam on Rice Genome: Transposon Activation.Genes (Basel). 2023 Dec 4;14(12):2178. doi: 10.3390/genes14122178. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38137000 Free PMC article.
-
Widespread HCD-tRNA derived SINEs in bivalves rely on multiple LINE partners and accumulate in genic regions.Mob DNA. 2024 Oct 16;15(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s13100-024-00332-x. Mob DNA. 2024. PMID: 39415259 Free PMC article.
-
A benchmark of transposon insertion detection tools using real data.Mob DNA. 2019 Dec 30;10:53. doi: 10.1186/s13100-019-0197-9. eCollection 2019. Mob DNA. 2019. PMID: 31892957 Free PMC article.
-
On the Importance to Acknowledge Transposable Elements in Epigenomic Analyses.Genes (Basel). 2019 Mar 31;10(4):258. doi: 10.3390/genes10040258. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30935103 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bartolom� C, Maside X, Charlesworth B. 2002. On the abundance and distribution of transposable elements in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Biol Evol. 19:926–937. - PubMed
-
- Brennecke J, et al.2007. Discrete small RNA-generating loci as master regulators of transposon activity in Drosophila. Cell 128:1089–1103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

