Identification of EGFLAM, SPATC1L and RNASE13 as novel susceptibility loci for aortic aneurysm in Japanese individuals by exome-wide association studies
- PMID: 28339009
- PMCID: PMC5403497
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.2927
Identification of EGFLAM, SPATC1L and RNASE13 as novel susceptibility loci for aortic aneurysm in Japanese individuals by exome-wide association studies
Abstract
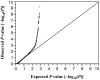
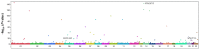
We performed an exome-wide association study (EWAS) to identify genetic variants - in particular, low‑frequency or rare variants with a moderate to large effect size - that confer susceptibility to aortic aneurysm with 8,782 Japanese subjects (456 patients with aortic aneurysm, 8,326 control individuals) and with the use of Illumina HumanExome-12 DNA Analysis BeadChip or Infinium Exome-24 BeadChip arrays. The correlation of allele frequencies for 41,432 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that passed quality control to aortic aneurysm was examined with Fisher's exact test. Based on Bonferroni's correction, a P-value of <1.21x10-6 was considered statistically significant. The EWAS revealed 59 SNPs that were significantly associated with aortic aneurysm. None of these SNPs was significantly (P<2.12x10-4) associated with aortic aneurysm by multivariable logistic regression analysis with adjustment for age, gender and hypertension, although 8 SNPs were related (P<0.05) to this condition. Examination of the correlation of these latter 8 SNPs to true or dissecting aortic aneurysm separately showed that rs1465567 [T/C (W229R)] of the EGF-like, fibronectin type III, and laminin G domains gene (EGFLAM) (dominant model; P=0.0014; odds ratio, 1.63) was significantly (P<0.0016) associated with true aortic aneurysm. We next performed EWASs for true or dissecting aortic aneurysm separately and found that 45 and 19 SNPs were significantly associated with these conditions, respectively. Multivariable logistic regression analysis with adjustment for covariates revealed that rs113710653 [C/T (E231K)] of the spermatogenesis- and centriole associated 1-like gene (SPATC1L) (dominant model; P=0.0002; odds ratio, 5.32) and rs143881017 [C/T (R140H)] of the ribonuclease A family member 13 gene (RNASE13) (dominant model; P=0.0006; odds ratio, 5.77) were significantly (P<2.78x10-4 or P<6.58x10-4, respectively) associated with true or dissecting aortic aneurysm, respectively. EGFLAM and SPATC1L may thus be susceptibility loci for true aortic aneurysm and RNASE13 may be such a locus for dissecting aneurysm in Japanese individuals.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of TNFSF13, SPATC1L, SLC22A25 and SALL4 as novel susceptibility loci for atrial fibrillation by an exome‑wide association study.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Nov;16(5):5823-5832. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.7334. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28849223 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of six polymorphisms as novel susceptibility loci for ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke by exome-wide association studies.Int J Mol Med. 2017 Jun;39(6):1477-1491. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.2972. Epub 2017 May 3. Int J Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28487959 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of STXBP2 as a novel susceptibility locus for myocardial infarction in Japanese individuals by an exome-wide association study.Oncotarget. 2017 May 16;8(20):33527-33535. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16536. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28380445 Free PMC article.
-
[Progress in genetic study of aortic dissection].Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2013 Aug;30(4):435-8. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1003-9406.2013.04.012. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23926011 Review. Chinese.
-
Aortic aneurysms: an immune disease with a strong genetic component.Circulation. 2008 Jan 15;117(2):242-52. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.690982. Circulation. 2008. PMID: 18195185 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Integrated bioinformatics analysis reveals novel key biomarkers and potential candidate small molecule drugs in gestational diabetes mellitus.Biosci Rep. 2021 May 28;41(5):BSR20210617. doi: 10.1042/BSR20210617. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33890634 Free PMC article.
-
Whole Exome Sequencing of a Patient with a Milder Phenotype of Xeroderma Pigmentosum Group C.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Apr 3;59(4):699. doi: 10.3390/medicina59040699. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37109656 Free PMC article.
-
Single nucleotide polymorphisms in piRNA-pathway genes: an insight into genetic determinants of human diseases.Mol Genet Genomics. 2020 Jan;295(1):1-12. doi: 10.1007/s00438-019-01612-5. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Mol Genet Genomics. 2020. PMID: 31612310 Review.
-
EGFLAM correlates with cell proliferation, migration, invasion and poor prognosis in glioblastoma.Cancer Biomark. 2019;24(3):343-350. doi: 10.3233/CBM-181740. Cancer Biomark. 2019. PMID: 30829611 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Association Study of Alopecia Areata in Taiwan: The Conflict Between Individuals and Hair Follicles.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023 Sep 21;16:2597-2612. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S428788. eCollection 2023. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37752970 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schwarze U, Schievink WI, Petty E, Jaff MR, Babovic-Vuksanovic D, Cherry KJ, Pepin M, Byers PH. Haploinsufficiency for one COL3A1 allele of type III procollagen results in a phenotype similar to the vascular form of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV. Am J Hum Genet. 2001;69:989–1001. doi: 10.1086/324123. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

