The effects of interleukin-2 on immune response regulation
- PMID: 28339682
- PMCID: PMC5576036
- DOI: 10.1093/imammb/dqw021
The effects of interleukin-2 on immune response regulation
Abstract
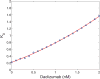
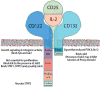
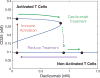
The immune system has many adaptive and dynamic components that are regulated to ensure appropriate, precise and rapid response to a foreign pathogen. A delayed or inadequate immune response can lead to prolonged disease, while an excessive or under-regulated response can lead to autoimmunity. The cytokine, interleukin-2 (IL-2) and its receptor IL-2R play an important role in maintaining this balance.The IL-2 receptor transduces pSTAT5 signal through both the intermediate and high affinity receptors, which differ from each other by the presence of CD25 chain in IL-2 receptor. We present experimental data on the kinetics of pSTAT5 signalling through both of the receptors and develop a model that captures this kinetics. We then use this model to parameterize key aspects of two additional models in which we propose and study two different mechanisms by which IL-2 receptor can transduce distinct signals leading to either an activated or a non-activated cell state. We speculate that this initial state differentiation, perhaps enhanced by downstream feedbacks, may eventually lead to differential cell fates.Our result shows that non-linear dynamical models can suggest resolution of a puzzling array of seemingly contradictory experimental results on IL-2 effect on proliferation and differentiation of T-cells.
Figures












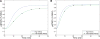



References
-
- Bielekova B, Catalfamo M, Reichert-Scrivner S, Packer A, Cerna M, Waldmann TA, McFarland H, Henkart PA, Martin R. Regulatory cd56(bright) natural killer cells mediate immunomodulatory effects of il-2ralpha-targeted therapy (daclizumab) in multiple sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:5941–5946. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bielekova B, Richert N, Howard T, Blevins G, Markovic-Plese S, McCartin J, Frank JA, Wurfel J, Ohayon J, Waldmann TA, McFarland HF, Martin R. Humanized anti-cd25 (daclizumab) inhibits disease activity in multiple sclerosis patients failing to respond to interferon beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:8705–8708. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

