Dietary resveratrol supplementation prevents transport-stress-impaired meat quality of broilers through maintaining muscle energy metabolism and antioxidant status
- PMID: 28339929
- PMCID: PMC5850463
- DOI: 10.3382/ps/pex004
Dietary resveratrol supplementation prevents transport-stress-impaired meat quality of broilers through maintaining muscle energy metabolism and antioxidant status
Abstract
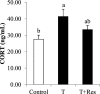
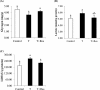
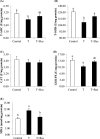
This experiment was to evaluate the effect of dietary resveratrol (Res) supplementation (0, 400 mg/kg) on growth performance, meat quality, and muscle anaerobic glycolysis and antioxidant capacity of transported broilers. A total of 360 21-day-old male Cobb broilers was randomly allotted to 2 dietary treatments (Res-free group and Res group) with 12 replicates of 15 birds each. On the morning of d 42, after a 9-hour fast, 24 birds (2 birds of each replicate) were selected from the Res-free group and then equally placed into 2 crates, and the other 12 birds (one bird of each replicate) were selected from the Res group and then placed into the other crate. All birds in the 3 crates were transported according to the following protocols: 0-hour transport of birds in the Res-free group (control group), 3-hour transport of birds in the Res-free group (T group), and 3-hour transport of birds in the Res group (T + Res group). The results showed that Res not only improved feed conversion ratio (P < 0.05) but also tended to improve birds' final body weight (P < 0.10). In the Res-free group, a 3-hour transport increased serum corticosterone concentration, muscle malondialdehyde (MDA) and lactate contents, and muscle lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity, while it decreased muscle glycogen content, total superoxide dismutase (T-SOD), and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-PX) activities (P < 0.05), which induced decreased breast meat quality (lower pH24h and higher drip loss and L*24 h, P < 0.05). Nevertheless, compared with the T group, Res increased muscle glycogen content and T-SOD and GSH-PX activities (P < 0.05 or P < 0.10), while it decreased muscle MDA content and LDH activity (P < 0.05), which is beneficial to the meat quality maintenance of transported broilers (lower drip loss, L*24 h, and higher pH24h, P < 0.05 or P < 0.10). This study provides the first evidence that dietary resveratrol supplementation prevents transport-stress-impaired meat quality of broilers, possibly through decreasing the muscle anaerobic glycolysis metabolism and improving the muscle antioxidant capacity.
Keywords: antioxidant capacity; broiler; meat quality; resveratrol; transport stress.
© The Authors 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Poultry Science Association.
Figures
References
-
- Alagawany M. M., Farag M. R., Dhama K., Abd El-Hack M. E., Tiwari R., Alam G. M.. 2015. Mechanisms and beneficial applications of resveratrol as feed additive in animal and poultry nutrition: A review. Int. J. Pharmacol. 11:213–221.
-
- Dadgar S., Lee E. S., Leer T. L., Burlinguette N., Classen H. L., Crowe T. G., Shand P. J.. 2010. Effect of microclimate temperature during transportation of broiler chickens on quality of the pectoralis major muscle. Poult. Sci. 89:1033–1041. - PubMed
-
- Goliomytis M., Tsoureki D., Simitzis P. E., Charismiadou M. A., Hager-Theodorides A. L., Deligeorgis S. G.. 2014. The effects of quercetin dietary supplementation on broiler growth performance, meat quality, and oxidative stability. Poult. Sci. 93:1957–1962. - PubMed
-
- Kamboh A. A., Zhu W. Y.. 2013. Individual and combined effects of genistein and hesperidin supplementation on meat quality in meat-type broiler chickens. J. Sci. Food Agric. 93:3362–3367. - PubMed
-
- Kannan G., Heath J. L., Wabeck C. J., Souza M. C., Howe J. C., Mench J. A.. 1997. Effects of crating and transport on stress and meat quality characteristics in broilers. Poult. Sci. 76:523–529. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

