Oral ghrelin receptor agonist MK-0677 increases serum insulin-like growth factor 1 in hemodialysis patients: a randomized blinded study
- PMID: 28340044
- PMCID: PMC6019053
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfw474
Oral ghrelin receptor agonist MK-0677 increases serum insulin-like growth factor 1 in hemodialysis patients: a randomized blinded study
Abstract
Background: Protein-energy wasting (PEW) in end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients is associated with increased morbidity and mortality, but options for treatment are limited. Growth hormone (GH) increases insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), with improved nutritional parameters, but must be given subcutaneously and does not provide normal GH secretion patterns. MK-0677, an oral ghrelin receptor agonist (GRA), maintains normal GH secretion and increases lean body mass in normal subjects; it has not been studied in dialysis patients, an essential step in assessing efficacy and safety prior to clinical trials.
Methods: We performed a randomized crossover double-blind study in assessing the effect of MK-0677 versus placebo on IGF-1 levels, the primary outcome, in hemodialysis patients. In total, 26 subjects enrolled and 22 completed the 3-month crossover study.
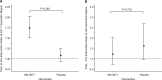
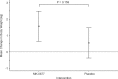
Results: The geometric mean IGF-1 was 1.07-fold greater [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.89-1.27; P = 0.718] after placebo. In patients receiving MK-0677, the geometric mean IGF-1 were 1.76-fold greater (95% CI 1.48-2.10; P < 0.001) following MK-0677. When the data were adjusted for preintervention IGF-1 concentration, the ratio of geometric means (MK-0677 relative to placebo) for the pre- versus postintervention change in the IGF-1 was 1.65 (95% CI 1.33-2.04; P < 0.001). These data demonstrate a 65% greater increase (95% CI 33-104%) in IGF-1 in MK-0677-dosed subjects compared with placebo. There were no serious adverse effects attributable to MK-0677.
Conclusions: MK-0677 increased serum IGF-1 levels with minimal adverse effects in hemodialysis subjects. Studies are needed to evaluate whether long-term therapy with MK-0677 improves PEW, lean body mass, physical strength, quality of life and survival in CKD/ESRD patients.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Ikizler TA. Nutrition, inflammation and chronic kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 2008; 17: 162–167 - PubMed
-
- Muscaritoli M, Molfino A, Bollea MR. et al. Malnutrition and wasting in renal disease. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2009; 12: 378–383 - PubMed
-
- Fouque D, Pelletier S, Mafra D. et al. Nutrition and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 2011; 80: 348–357 - PubMed
-
- Fleischmann E, Teal N, Dudley J. et al. Influence of excess weight on mortality and hospital stay in 1346 hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 1999; 55: 1560–1567 - PubMed
-
- Goldwasser P, Mittman N, Antignani A. et al. Predictors of mortality in hemodialysis patients [abstract]. J Am Soc Nephrol 1993; 3: 1613–1622 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

