A Phase Separation Model for Transcriptional Control
- PMID: 28340338
- PMCID: PMC5432200
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.02.007
A Phase Separation Model for Transcriptional Control
Abstract
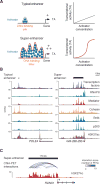
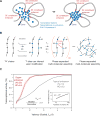
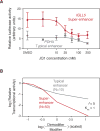
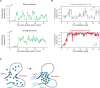
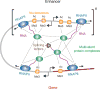
Phase-separated multi-molecular assemblies provide a general regulatory mechanism to compartmentalize biochemical reactions within cells. We propose that a phase separation model explains established and recently described features of transcriptional control. These features include the formation of super-enhancers, the sensitivity of super-enhancers to perturbation, the transcriptional bursting patterns of enhancers, and the ability of an enhancer to produce simultaneous activation at multiple genes. This model provides a conceptual framework to further explore principles of gene control in mammals.
Keywords: bursting; co-operativity; enhancer; gene control; nuclear body; phase separation; super-enhancer; transcription; transcriptional burst.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Banerji J, Rusconi S, Schaffner W. Expression of a beta-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell. 1981;27:299–308. - PubMed
-
- Benoist C, Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981;290:304–310. - PubMed
-
- Bergeron-Sandoval LP, Safaee N, Michnick SW. Mechanisms and Consequences of Macromolecular Phase Separation. Cell. 2016;165:1067–1079. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

