Targeted Apoptosis of Senescent Cells Restores Tissue Homeostasis in Response to Chemotoxicity and Aging
- PMID: 28340339
- PMCID: PMC5556182
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.02.031
Targeted Apoptosis of Senescent Cells Restores Tissue Homeostasis in Response to Chemotoxicity and Aging
Abstract
The accumulation of irreparable cellular damage restricts healthspan after acute stress or natural aging. Senescent cells are thought to impair tissue function, and their genetic clearance can delay features of aging. Identifying how senescent cells avoid apoptosis allows for the prospective design of anti-senescence compounds to address whether homeostasis can also be restored. Here, we identify FOXO4 as a pivot in senescent cell viability. We designed a FOXO4 peptide that perturbs the FOXO4 interaction with p53. In senescent cells, this selectively causes p53 nuclear exclusion and cell-intrinsic apoptosis. Under conditions where it was well tolerated in vivo, this FOXO4 peptide neutralized doxorubicin-induced chemotoxicity. Moreover, it restored fitness, fur density, and renal function in both fast aging XpdTTD/TTD and naturally aged mice. Thus, therapeutic targeting of senescent cells is feasible under conditions where loss of health has already occurred, and in doing so tissue homeostasis can effectively be restored.
Keywords: FOXO4; IL6; LMNB1; Senescence; TP53; aging; apoptosis; cell-penetrating peptide; chemotherapy; tissue homeostasis.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

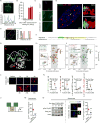
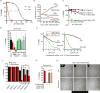
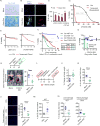

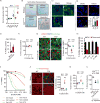

Comment in
-
Ageing: Targeting senescence-associated tissue damage.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017 Jun;13(6):319. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2017.53. Epub 2017 Apr 10. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28392563 No abstract available.
-
Ageing: Tools to eliminate senescent cells.Nature. 2017 May 18;545(7654):294-296. doi: 10.1038/nature22493. Epub 2017 May 10. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28489828 No abstract available.
Comment on
-
Rejuvenation by Therapeutic Elimination of Senescent Cells.Cell. 2017 Mar 23;169(1):3-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.03.014. Cell. 2017. PMID: 28340347
References
-
- Beydoun T, Deloche C, Perino J, Kirwan BA, Combette JM, Behar-Cohen F. Subconjunctival injection of XG-102, a JNK inhibitor peptide, in patients with intraocular inflammation: a safety and tolerability study. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2015;31:93–99. - PubMed
-
- Borsello T, Clarke PG, Hirt L, Vercelli A, Repici M, Schorderet DF, Bogousslavsky J, Bonny C. A peptide inhibitor of c-Jun N-terminal kinase protects against excitotoxicity and cerebral ischemia. Nat Med. 2003;9:1180–1186. - PubMed
-
- Brown JP, Wei W, Sedivy JM. Bypass of senescence after disruption of p21CIP1/WAF1 gene in normal diploid human fibroblasts. Science. 1997;277:831–834. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

