Improved Outcomes with Modern Lung-Sparing Trimodality Therapy in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
- PMID: 28341225
- PMCID: PMC5499250
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtho.2017.02.026
Improved Outcomes with Modern Lung-Sparing Trimodality Therapy in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
Abstract
Introduction: Higher target conformity and better sparing of organs at risk with modern radiotherapy (RT) may result in higher tumor control and less toxicity. In this study, we compare our institutional multimodality therapy experience of adjuvant chemotherapy and hemithoracic intensity-modulated pleural RT (IMPRINT) with previously used adjuvant conventional RT (CONV) in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) treated with lung-sparing pleurectomy/decortication (P/D).
Methods: We analyzed 209 patients who underwent P/D and adjuvant RT (131 who received CONV and 78 who received IMPRINT) for MPM between 1974 and 2015. The primary end point was overall survival (OS). The Kaplan-Meier method and Cox proportional hazards model were used to calculate OS; competing risks analysis was performed for local failure-free survival and progression-free survival. Univariate analysis and multivariate analysis were performed with relevant clinical and treatment factors.
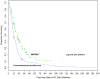
Results: The median age was 64 years, and 80% of the patients were male. Patients receiving IMPRINT had significantly higher rates of the epithelial histological type, advanced pathological stage, and chemotherapy treatment. OS was significantly higher after IMPRINT (median 20.2 versus 12.3 months, p = 0.001). Higher Karnofsky performance score, epithelioid histological type, macroscopically complete resection, and use of chemotherapy/IMPRINT were found to be significant factors for longer OS in multivariate analysis. No significant predictive factors were identified for local failure or progression. Grade 2 or higher esophagitis developed in fewer patients after IMPRINT than after CONV (23% versus 47%).
Conclusions: Trimodality therapy including adjuvant hemithoracic IMPRINT, chemotherapy, and P/D is associated with promising OS rates and decreased toxicity in patients with MPM. Dose constraints should be applied vigilantly to minimize serious adverse events.
Keywords: Conventional RT; IMPRINT; Intensity-modulated pleural radiation therapy; Malignant pleural mesothelioma; Pleurectomy/decortication.
Copyright © 2017 International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest and Source of Funding: No relevant conflicts of interest were declared. This research was supported in part by an NIH Core Grant P30 CA008748
Figures
Comment in
-
Pleural IMRT after Lung-Sparing Cytoreduction for Mesothelioma: Mature Enough to Randomize.J Thorac Oncol. 2017 Jun;12(6):919-921. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2017.04.013. J Thorac Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28532562 No abstract available.
-
Strike or Spare? A Review of Lung-Sparing Therapies for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021 Jun 1;110(2):257-260. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2021.02.016. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021. PMID: 33989566 No abstract available.
References
-
- Batirel HF, Metintas M, Caglar HB, et al. Adoption of pleurectomy and decortication for malignant mesothelioma leads to similar survival as extrapleural pneumonectomy. The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery. 2016;151:478–484. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2015.09.121. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Burt BM, Cameron RB, Mollberg NM, et al. Malignant pleural mesothelioma and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons Database: an analysis of surgical morbidity and mortality. The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery. 2014;148:30–35. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2014.03.011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cao C, Tian D, Park J, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of surgical treatments for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Lung Cancer. 2014;83:240–245. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2013.11.026. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Flores RM, Pass HI, Seshan VE, et al. Extrapleural pneumonectomy versus pleurectomy/decortication in the surgical management of malignant pleural mesothelioma: Results in 663 patients. The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery. 2008;135:620–626. 626.e621–623. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2007.10.054. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hasegawa S. Extrapleural pneumonectomy or pleurectomy/decortication for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;62:516–521. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11748-014-0389-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical