A Low-Frequency Inactivating AKT2 Variant Enriched in the Finnish Population Is Associated With Fasting Insulin Levels and Type 2 Diabetes Risk
- PMID: 28341696
- PMCID: PMC5482074
- DOI: 10.2337/db16-1329
A Low-Frequency Inactivating AKT2 Variant Enriched in the Finnish Population Is Associated With Fasting Insulin Levels and Type 2 Diabetes Risk
Abstract
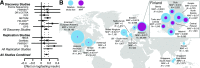
To identify novel coding association signals and facilitate characterization of mechanisms influencing glycemic traits and type 2 diabetes risk, we analyzed 109,215 variants derived from exome array genotyping together with an additional 390,225 variants from exome sequence in up to 39,339 normoglycemic individuals from five ancestry groups. We identified a novel association between the coding variant (p.Pro50Thr) in AKT2 and fasting plasma insulin (FI), a gene in which rare fully penetrant mutations are causal for monogenic glycemic disorders. The low-frequency allele is associated with a 12% increase in FI levels. This variant is present at 1.1% frequency in Finns but virtually absent in individuals from other ancestries. Carriers of the FI-increasing allele had increased 2-h insulin values, decreased insulin sensitivity, and increased risk of type 2 diabetes (odds ratio 1.05). In cellular studies, the AKT2-Thr50 protein exhibited a partial loss of function. We extend the allelic spectrum for coding variants in AKT2 associated with disorders of glucose homeostasis and demonstrate bidirectional effects of variants within the pleckstrin homology domain of AKT2.
© 2017 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures



References
-
- Kahn SE, Hull RL, Utzschneider KM. Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 2006;444:840–846 - PubMed
-
- Phillips DI, Clark PM, Hales CN, Osmond C. Understanding oral glucose tolerance: comparison of glucose or insulin measurements during the oral glucose tolerance test with specific measurements of insulin resistance and insulin secretion. Diabet Med 1994;11:286–292 - PubMed
-
- Manning AK, Hivert MF, Scott RA, et al.; DIAbetes Genetics Replication And Meta-analysis (DIAGRAM) Consortium; Multiple Tissue Human Expression Resource (MUTHER) Consortium . A genome-wide approach accounting for body mass index identifies genetic variants influencing fasting glycemic traits and insulin resistance. Nat Genet 2012;44:659–669 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K24 DK110550/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH107666/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA033684/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- G0601966/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK073541/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK098722/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101820/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101822/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM115428/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- MR/M501633/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 DK085501/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK078616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG042188/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NF-SI-0611-10219/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- R01 DK093757/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG046949/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K002414/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- Z01 HG000024/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085524/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K12 CA139160/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085545/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA006227/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK106236/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101782/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 200837/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 DK098032/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101810/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G0700931/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH101819/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201300048C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG000040/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007753/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090936/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L01341X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12015/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL102830/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12015/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HHSN268201300049C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK066358/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 DK088389/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK080140/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201300047C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085526/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201300050C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085584/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MR/M501633/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P01 AG027734/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK078616/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 098395/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 MH090951/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG038072/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101825/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090948/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090941/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K007017/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HHSN268201300046C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 095101/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- P30 DK092949/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001C/RC/CCR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK105561/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_13040/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH090937/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007055/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0601261/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HHSN268201000029C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001E/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101814/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RP-PG-0407-10371/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- P30 DK020595/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

