Endogenous prostaglandin E2 amplifies IL-33 production by macrophages through an E prostanoid (EP)2/EP4-cAMP-EPAC-dependent pathway
- PMID: 28341741
- PMCID: PMC5437228
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.769422
Endogenous prostaglandin E2 amplifies IL-33 production by macrophages through an E prostanoid (EP)2/EP4-cAMP-EPAC-dependent pathway
Abstract
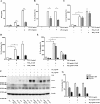
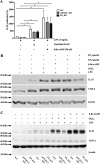
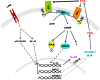
When activated through toll-like receptors (TLRs), macrophages generate IL-33, an IL-1 family member that induces innate immune responses through ST2 signaling. LPS, a TLR4 ligand, induces macrophages to generate prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) through inducible COX-2 and microsomal PGE2 synthase 1 (mPGES-1) (1). We demonstrate that IL-33 production by bone marrow-derived murine macrophages (bmMFs) requires the generation of endogenous PGE2 and the intrinsic expression of EP2 receptors to amplify NF-κB-dependent, LPS-induced IL-33 expression via exchange protein activated by cAMP (EPAC). Compared with WT cells, bmMFs lacking either mPGES-1 or EP2 receptors displayed reduced LPS-induced IL-33 levels. A selective EP2 agonist and, to a lesser extent, EP4 receptor agonist potentiated LPS-induced IL-33 generation from both mPGES-1-null and WT bmMFs, whereas EP1 and EP3 receptor agonists were inactive. The effects of PGE2 depended on cAMP, were mimicked by an EPAC-selective agonist, and were attenuated by EPAC-selective antagonism and knockdown. LPS-induced p38 MAPK and NF-κB activations were necessary for both IL-33 production and PGE2 generation, and exogenous PGE2 partly reversed the suppression of IL-33 production caused by p38 MAPK and NF-κB inhibition. Mice lacking mPGES-1 showed lower IL-33 levels and attenuated lung inflammation in response to repetitive Alternaria inhalation challenges. Cumulatively, our data demonstrate that endogenous PGE2, EP2 receptors, and EPAC are prerequisites for maximal LPS-induced IL-33 expression and that exogenous PGE2 can amplify IL-33 production via EP2 and EP4 receptors. The ubiquitous induction of mPGES-1-dependent PGE2 may be crucial for innate immune system activation during various IL-33 driven pathologic disorders.
Keywords: EPAC; IL-33; PGE2; bone marrow macrophages; cAMP; cytokine; innate immunity; mPGES-1; macrophage; prostaglandin.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures


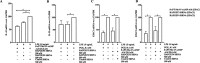


Similar articles
-
Differential expression of E-type prostanoid receptors 2 and 4 in microglia stimulated with lipopolysaccharide.J Neuroinflammation. 2017 Jan 5;14(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0780-7. J Neuroinflammation. 2017. PMID: 28086956 Free PMC article.
-
Prostaglandin E2 Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation through EP4 Receptor and Intracellular Cyclic AMP in Human Macrophages.J Immunol. 2015 Jun 1;194(11):5472-5487. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401343. Epub 2015 Apr 27. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25917098 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Role of mPGES-1 (Microsomal Prostaglandin E Synthase-1)-Derived PGE2 (Prostaglandin E2) and the Endothelial EP4 (Prostaglandin E Receptor) in Vascular Responses to Injury.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 May;38(5):1115-1124. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.310713. Epub 2018 Mar 29. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018. PMID: 29599139 Free PMC article.
-
[Cooperation of two subtypes of PGE2 receptor, Gi coupled EP3 and Gs coupled EP2 or EP4 subtype].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2003 Oct;123(10):837-43. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.123.837. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2003. PMID: 14577329 Review. Japanese.
-
Targeting EP2 Receptor for Drug Discovery: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats (SWOT) Analysis.J Med Chem. 2023 Jul 27;66(14):9313-9324. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00655. Epub 2023 Jul 17. J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37458373 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tricarboxylic acid cycle metabolites: new players in macrophage.Inflamm Res. 2024 Apr;73(4):531-539. doi: 10.1007/s00011-024-01853-0. Epub 2024 Mar 18. Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38498178 Review.
-
Heat-Labile Enterotoxin Decreases Macrophage Phagocytosis of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli.Microorganisms. 2023 Aug 21;11(8):2121. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11082121. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37630681 Free PMC article.
-
IL-33, an Alarmin of the IL-1 Family Involved in Allergic and Non Allergic Inflammation: Focus on the Mechanisms of Regulation of Its Activity.Cells. 2021 Dec 30;11(1):107. doi: 10.3390/cells11010107. Cells. 2021. PMID: 35011670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid Profile of Activated Macrophages and Contribution of Group V Phospholipase A2.Biomolecules. 2020 Dec 29;11(1):25. doi: 10.3390/biom11010025. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 33383652 Free PMC article.
-
Correlative Study on Impaired Prostaglandin E2 Regulation in Epicardial Adipose Tissue and its Role in Maladaptive Cardiac Remodeling via EPAC2 and ST2 Signaling in Overweight Cardiovascular Disease Subjects.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 14;21(2):520. doi: 10.3390/ijms21020520. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31947646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hardman C., and Ogg G. (2016) Interleukin-33, friend and foe in type-2 immune responses. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 42, 16–24 - PubMed
-
- Baekkevold E. S., Roussigné M., Yamanaka T., Johansen F.-E., Jahnsen F. L., Amalric F., Brandtzaeg P., Erard M., Haraldsen G., and Girard J.-P. (2003) Molecular characterization of NF-HEV, a nuclear factor preferentially expressed in human high endothelial venules. Am. J. Pathol. 163, 69–79 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

