Endogenous prostaglandin E2 amplifies IL-33 production by macrophages through an E prostanoid (EP)2/EP4-cAMP-EPAC-dependent pathway
- PMID: 28341741
- PMCID: PMC5437228
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.769422
Endogenous prostaglandin E2 amplifies IL-33 production by macrophages through an E prostanoid (EP)2/EP4-cAMP-EPAC-dependent pathway
Abstract
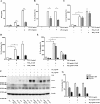
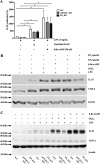
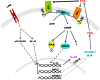
When activated through toll-like receptors (TLRs), macrophages generate IL-33, an IL-1 family member that induces innate immune responses through ST2 signaling. LPS, a TLR4 ligand, induces macrophages to generate prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) through inducible COX-2 and microsomal PGE2 synthase 1 (mPGES-1) (1). We demonstrate that IL-33 production by bone marrow-derived murine macrophages (bmMFs) requires the generation of endogenous PGE2 and the intrinsic expression of EP2 receptors to amplify NF-κB-dependent, LPS-induced IL-33 expression via exchange protein activated by cAMP (EPAC). Compared with WT cells, bmMFs lacking either mPGES-1 or EP2 receptors displayed reduced LPS-induced IL-33 levels. A selective EP2 agonist and, to a lesser extent, EP4 receptor agonist potentiated LPS-induced IL-33 generation from both mPGES-1-null and WT bmMFs, whereas EP1 and EP3 receptor agonists were inactive. The effects of PGE2 depended on cAMP, were mimicked by an EPAC-selective agonist, and were attenuated by EPAC-selective antagonism and knockdown. LPS-induced p38 MAPK and NF-κB activations were necessary for both IL-33 production and PGE2 generation, and exogenous PGE2 partly reversed the suppression of IL-33 production caused by p38 MAPK and NF-κB inhibition. Mice lacking mPGES-1 showed lower IL-33 levels and attenuated lung inflammation in response to repetitive Alternaria inhalation challenges. Cumulatively, our data demonstrate that endogenous PGE2, EP2 receptors, and EPAC are prerequisites for maximal LPS-induced IL-33 expression and that exogenous PGE2 can amplify IL-33 production via EP2 and EP4 receptors. The ubiquitous induction of mPGES-1-dependent PGE2 may be crucial for innate immune system activation during various IL-33 driven pathologic disorders.
Keywords: EPAC; IL-33; PGE2; bone marrow macrophages; cAMP; cytokine; innate immunity; mPGES-1; macrophage; prostaglandin.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures


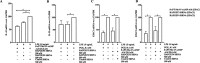


References
-
- Hardman C., and Ogg G. (2016) Interleukin-33, friend and foe in type-2 immune responses. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 42, 16–24 - PubMed
-
- Baekkevold E. S., Roussigné M., Yamanaka T., Johansen F.-E., Jahnsen F. L., Amalric F., Brandtzaeg P., Erard M., Haraldsen G., and Girard J.-P. (2003) Molecular characterization of NF-HEV, a nuclear factor preferentially expressed in human high endothelial venules. Am. J. Pathol. 163, 69–79 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

