Adductome-based identification of biomarkers for lipid peroxidation
- PMID: 28341743
- PMCID: PMC5437230
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.762609
Adductome-based identification of biomarkers for lipid peroxidation
Abstract
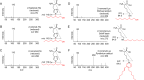
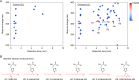
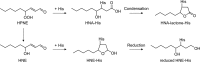
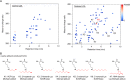
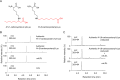
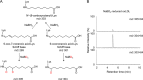
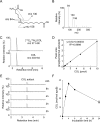
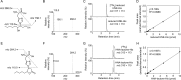
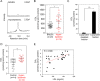
Lipid peroxidation is an endogenous source of aldehydes that gives rise to covalent modification of proteins in various pathophysiological states. In this study, a strategy for the comprehensive detection and comparison of adducts was applied to find a biomarker for lipid peroxidation-modified proteins in vivo This adductome approach utilized liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS/MS) methods designed to detect the specific product ions from positively ionized adducts in a selected reaction monitoring mode. Using this procedure, we comprehensively analyzed lysine and histidine adducts generated in the in vitro oxidized low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and observed a prominent increase in several adducts, including a major lysine adduct. Based on the high resolution ESI-MS of the adduct and on the LC-ESI-MS/MS analysis of the synthetic adduct candidates, the major lysine adduct detected in the oxidized LDL was identified as Nϵ-(8-carboxyoctanyl)lysine (COL). Strikingly, a significantly higher amount of COL was detected in the sera from atherosclerosis-prone mice and from patients with hyperlipidemia compared with the controls. These data not only offer structural insights into protein modification by lipid peroxidation products but also provide a platform for the discovery of biomarkers for human diseases.
Keywords: aldehyde; biomarker; lipid oxidation; lipoprotein; mass spectrometry (MS); protein chemical modification.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures



References
-
- Gutteridge J. M., and Halliwell B. (1990) The measurement and mechanism of lipid peroxidation in biological systems. Trends Biochem. Sci. 15, 129–135 - PubMed
-
- Esterbauer H., Schaur R. J., and Zollner H. (1991) Chemistry and biochemistry of 4-hydroxynonenal, malonaldehyde and related aldehydes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 11, 81–128 - PubMed
-
- Uchida K. (2003) Histidine and lysine as targets of oxidative modification. Amino Acids 25, 249–257 - PubMed
-
- Steinberg D., Parthasarathy S., Carew T. E., Khoo J. C., and Witztum J. L. (1989) Beyond cholesterol. Modifications of low-density lipoprotein that increase its atherogenicity. N. Engl. J. Med. 320, 915–924 - PubMed
-
- Steinberg D. (1995) Role of oxidized LDL and antioxidants in atherosclerosis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 369, 39–48 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

