Protein CoAlation: a redox-regulated protein modification by coenzyme A in mammalian cells
- PMID: 28341808
- PMCID: PMC5509381
- DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20170129
Protein CoAlation: a redox-regulated protein modification by coenzyme A in mammalian cells
Abstract
Coenzyme A (CoA) is an obligatory cofactor in all branches of life. CoA and its derivatives are involved in major metabolic pathways, allosteric interactions and the regulation of gene expression. Abnormal biosynthesis and homeostasis of CoA and its derivatives have been associated with various human pathologies, including cancer, diabetes and neurodegeneration. Using an anti-CoA monoclonal antibody and mass spectrometry, we identified a wide range of cellular proteins which are modified by covalent attachment of CoA to cysteine thiols (CoAlation). We show that protein CoAlation is a reversible post-translational modification that is induced in mammalian cells and tissues by oxidising agents and metabolic stress. Many key cellular enzymes were found to be CoAlated in vitro and in vivo in ways that modified their activities. Our study reveals that protein CoAlation is a widespread post-translational modification which may play an important role in redox regulation under physiological and pathophysiological conditions.
Keywords: coenzyme A; metabolic and oxidative stress; post-translational modification; proteomics.
© 2017 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures

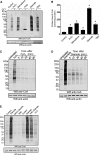
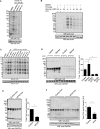



Comment in
-
Protein CoAlation: a redox-linked post-translational modification.Biochem J. 2017 Aug 10;474(16):2897-2899. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170168. Biochem J. 2017. PMID: 28798160
References
-
- Robishaw J.D., Berkich D. and Neely J.R. (1982) Rate-limiting step and control of coenzyme A synthesis in cardiac muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 257, 10967–10972 PMID: - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MC_EX_MR/K015680/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MRC_MC_UU_12012/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U105663142/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/L010410/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12012/5/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RG/12/13/29853/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- 100574/Z/12/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MRC_MC_UU_12012/5/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 110158/Z/15/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_U105178788/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 110159/Z/15/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12012/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/L020874/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- 4050281695/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/H002731/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

