Tumour suppressor EP300, a modulator of paclitaxel resistance and stemness, is downregulated in metaplastic breast cancer
- PMID: 28341962
- PMCID: PMC5427146
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-017-4202-z
Tumour suppressor EP300, a modulator of paclitaxel resistance and stemness, is downregulated in metaplastic breast cancer
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Tumour suppressor EP300, a modulator of paclitaxel resistance and stemness, is downregulated in metaplastic breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018 Jan;167(2):605-606. doi: 10.1007/s10549-017-4633-6. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018. PMID: 29305809 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Purpose: We have previously described a novel pathway controlling drug resistance, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and stemness in breast cancer cells. Upstream in the pathway, three miRs (miR-106b, miR-93 and miR-25) target EP300, a transcriptional activator of E-cadherin. Upregulation of these miRs leads to the downregulation of EP300 and E-cadherin with initiation of an EMT. However, miRs regulate the expression of many genes, and the contribution to EMT by miR targets other than EP300 cannot be ruled out.
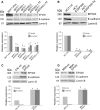
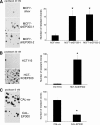
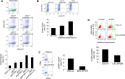
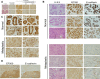
Methods: We used lentiviruses expressing EP300-targeting shRNA to downregulate its expression in MCF-7 cells as well as an EP300-knocked-out colon carcinoma cell line. An EP300-expression plasmid was used to upregulate its expression in basal-like CAL51 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Drug resistance was determined by short-term proliferation and long-term colony formation assays. Stemness was determined by tumour sphere formation in both soft agar and liquid cultures as well as by the expression of CD44/CD24/ALDH markers. Gene expression microarray analysis was performed in MCF-7 cells lacking EP300. EP300 expression was analysed by immunohistochemistry in 17 samples of metaplastic breast cancer.
Results: Cells lacking EP300 became more resistant to paclitaxel whereas EP300 overexpression increased their sensitivity to the drug. Expression of cancer stem cell markers, as well as tumour sphere formation, was also increased in EP300-depleted cells, and was diminished in EP300-overexpressing cells. The EP300-regulated gene signature highlighted genes associated with adhesion (CEACAM5), cytoskeletal remodelling (CAPN9), stemness (ABCG2), apoptosis (BCL2) and metastasis (TGFB2). Some genes in this signature were also validated in a previously generated EP300-depleted model of breast cancer using minimally transformed mammary epithelial cells. Importantly, two key genes in apoptosis and stemness, BCL2 and ABCG2, were also upregulated in EP300-knockout colon carcinoma cells and their paclitaxel-resistant derivatives. Immunohistochemical analysis demonstrated that EP300 expression was low in metaplastic breast cancer, a rare, but aggressive form of the disease with poor prognosis that is characterized by morphological and physiological features of EMT.
Conclusions: EP300 plays a major role in the reprogramming events, leading to a more malignant phenotype with the acquisition of drug resistance and cell plasticity, a characteristic of metaplastic breast cancer.
Keywords: ABCG2; BCL2; Cancer stem cells; Drug resistance; EP300 signature; Metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Imperial College Healthcare Tissue Bank (R14086) and Breast Cancer Now Tissue Bank (BCNTB-TR000054) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Figures



References
-
- Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, Campbell LL, Polyak K, Brisken C, Yang J, Weinberg RA. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell. 2008;133(4):704–715. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.03.027. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

