Clinical Trial of Vadadustat in Patients with Anemia Secondary to Stage 3 or 4 Chronic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 28343225
- PMCID: PMC5452283
- DOI: 10.1159/000464476
Clinical Trial of Vadadustat in Patients with Anemia Secondary to Stage 3 or 4 Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
Background: Therapeutic options for the treatment of anemia secondary to chronic kidney disease (CKD) remain limited. Vadadustat (AKB-6548) is an oral hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl-hydroxylase domain (HIF-PHD) inhibitor that is being investigated for the treatment of anemia secondary to CKD.
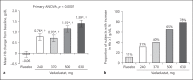
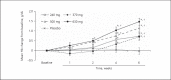
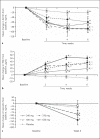
Methods: A phase 2a, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging trial (NCT01381094) was undertaken in adults with anemia secondary to CKD stage 3 or 4. Eligible subjects were evenly randomized to 5 groups: 240, 370, 500, or 630 mg of once-daily oral vadadustat or placebo for 6 weeks. All subjects received low-dose supplemental oral iron (50 mg daily). The primary endpoint was the mean absolute change in hemoglobin (Hb) from baseline to the end of treatment. Secondary endpoints included iron indices, safety, and tolerability.
Results: Ninety-three subjects were randomized. Compared with placebo, vadadustat significantly increased Hb after 6 weeks in a dose-dependent manner (analysis of variance; p < 0.0001). Vadadustat increased the total iron-binding capacity and decreased concentrations of ferritin and hepcidin. The proportion of subjects with at least 1 treatment-emergent adverse event was similar between vadadustat- and placebo-treated groups. No significant changes in blood pressure, vascular endothelial growth factor, C-reactive protein, or total cholesterol were observed. Limitations of this study included its small sample size and short treatment duration.
Conclusions: Vadadustat increased Hb levels and improved biomarkers of iron mobilization and utilization in patients with anemia secondary to stage 3 or 4 CKD. Global multicenter, randomized phase 3 trials are ongoing in non-dialysis-dependent and dialysis-dependent patients.
Keywords: Anemia; Chronic kidney disease; Clinical trials; Erythropoietin; Kidney disease.
© 2017 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
References
-
- Jones M, Ibels L, Schenkel B, Zagari M. Impact of epoetin alfa on clinical end points in patients with chronic renal failure: a meta-analysis. Kidney Int. 2004;65:757–767. - PubMed
-
- Locatelli F, Pisoni RL, Combe C, Bommer J, Andreucci VE, Piera L, Greenwood R, Feldman HI, Port FK, Held PJ. Anaemia in haemodialysis patients of five European countries: association with morbidity and mortality in the dialysis outcomes and practice patterns study (DOPPS) Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004;19:121–132. - PubMed
-
- Regidor DL, Kopple JD, Kovesdy CP, Kilpatrick RD, McAllister CJ, Aronovitz J, Greenland S, Kalantar-Zadeh K. Associations between changes in hemoglobin and administered erythropoiesis-stimulating agent and survival in hemodialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:1181–1191. - PubMed
-
- Besarab A, Bolton WK, Browne JK, Egrie JC, Nissenson AR, Okamoto DM, Schwab SJ, Goodkin DA. The effects of normal as compared with low hematocrit values in patients with cardiac disease who are receiving hemodialysis and epoetin. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:584–590. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

