Pancreatic alpha cell-selective deletion of Tcf7l2 impairs glucagon secretion and counter-regulatory responses to hypoglycaemia in mice
- PMID: 28343277
- PMCID: PMC5423960
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-017-4242-2
Pancreatic alpha cell-selective deletion of Tcf7l2 impairs glucagon secretion and counter-regulatory responses to hypoglycaemia in mice
Abstract
Aims/hypothesis: Transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) is a high mobility group (HMG) box-containing transcription factor and downstream effector of the Wnt signalling pathway. SNPs in the TCF7L2 gene have previously been associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes in genome-wide association studies. In animal studies, loss of Tcf7l2 function is associated with defective islet beta cell function and survival. Here, we explore the role of TCF7L2 in the control of the counter-regulatory response to hypoglycaemia by generating mice with selective deletion of the Tcf7l2 gene in pancreatic alpha cells.
Methods: Alpha cell-selective deletion of Tcf7l2 was achieved by crossing mice with floxed Tcf7l2 alleles to mice bearing a Cre recombinase transgene driven by the preproglucagon promoter (PPGCre), resulting in Tcf7l2AKO mice. Glucose homeostasis and hormone secretion in vivo and in vitro, and islet cell mass were measured using standard techniques.
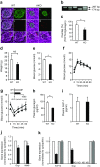
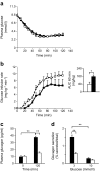
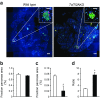
Results: While glucose tolerance was unaffected in Tcf7l2AKO mice, glucose infusion rates were increased (AUC for glucose during the first 60 min period of hyperinsulinaemic-hypoglycaemic clamp test was increased by 1.98 ± 0.26-fold [p < 0.05; n = 6] in Tcf7l2AKO mice vs wild-type mice) and glucagon secretion tended to be lower (plasma glucagon: 0.40 ± 0.03-fold vs wild-type littermate controls [p < 0.01; n = 6]). Tcf7l2AKO mice displayed reduced fasted plasma glucose concentration. Glucagon release at low glucose was impaired in islets isolated from Tcf7l2AKO mice (0.37 ± 0.02-fold vs islets from wild-type littermate control mice [p < 0.01; n = 6). Alpha cell mass was also reduced (72.3 ± 20.3% [p < 0.05; n = 7) in Tcf7l2AKO mice compared with wild-type mice.
Conclusions/interpretation: The present findings demonstrate an alpha cell-autonomous role for Tcf7l2 in the control of pancreatic glucagon secretion and the maintenance of alpha cell mass and function.
Keywords: Alpha cell; Diabetes; GWAS; Gene; Glucagon; Islet.
Conflict of interest statement
Data availability
Data are available on request from the authors.
Funding
GdSX thanks Diabetes UK (BDA 13/0004672), EFSD-MSD and Rosetrees Trust for Project grants. This work was funded by grants to GAR from Diabetes UK (Project BDA 11/0004210), the Wellcome Trust (Programme 081958/Z/07/Z; Senior Investigator Award WT098424AIA), and the MRC (UK; Project GO401641; Programme MR/J0003042/1). The work leading to this publication also received support from the Innovative Medicines Initiative Joint Undertaking under grant agreement no. 155005 (IMIDIA) (GAR, CM, PLH), resources of which are composed of a financial contribution from the European Union’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007–2013) and EFPIA companies’ in kind contribution.
Duality of interest
The authors declare that there is no duality of interest associated with this manuscript.
Contribution statement
GdSX and GAR conceived and designed the studies and co-wrote the article. PLH provided PPG
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

