Trismus following different treatment modalities for head and neck cancer: a systematic review of subjective measures
- PMID: 28343337
- PMCID: PMC5486547
- DOI: 10.1007/s00405-017-4519-6
Trismus following different treatment modalities for head and neck cancer: a systematic review of subjective measures
Abstract
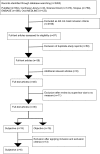
The aim of this review was to compare systematically the subjective measure of trismus between different interventions to treat head and neck cancer, particularly those of the oropharynx. Using The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) Guidelines, Six databases were searched for the text using various terms which include "oropharyngeal/head and neck cancer", "trismus/mouth opening" and the various treatment modalities. Included in the review were clinical studies (> or =10 patients). Three observers independently assessed the papers identified. Among the six studies reviewed, five showed a significantly worst outcome with regard to the quality-of-life questionnaire scores for a radiotherapy or surgery and radiotherapy (RT) ± chemotherapy or chemoradiotherapy when compared to surgery alone. Only one study showed no significant difference between surgery alone and other treatment modalities. Subjective quality-of-life measures are a concurrent part of modern surgical practice. Although subjective measures were utilised to measure post operative trismus successfully, there was no consensus as to which treatment modality had overall better outcomes, with conflicting studies in keeping with the current debate in this field. Larger and higher quality studies are needed to compare all three treatment modalities.
Keywords: Chemotherapy; Oropharyngeal carcinoma; Quality of life; Radiotherapy; Surgery; Trismus.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding
The authors did not receive any financial support or other external help in preparing this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
-
Interventions for the treatment of brain radionecrosis after radiotherapy or radiosurgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 9;7(7):CD011492. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011492.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29987845 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Valero's host index is useful in predicting radiation-induced trismus and osteoradionecrosis of the jaw risks in locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients.BMC Cancer. 2023 Jul 12;23(1):651. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11155-z. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37438683 Free PMC article.
-
Myofascial Induction Therapy Improves the Sequelae of Medical Treatment in Head and Neck Cancer Survivors: A Single-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Cross-Over Study.J Clin Med. 2021 Oct 27;10(21):5003. doi: 10.3390/jcm10215003. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34768520 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of life, craniomandibular function, and psychosocial factors related to pain and movement in patients with head and neck cancer.Support Care Cancer. 2024 May 9;32(6):334. doi: 10.1007/s00520-024-08518-y. Support Care Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38722345
-
Evaluation of recurrence, mortality and treatment complications of oral squamous cell carcinoma in public health centers in Shiraz during 2010 to 2020.BMC Oral Health. 2023 May 30;23(1):341. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03071-2. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37254138 Free PMC article.
-
Translation and Validation of the Gothenburg Trismus Questionnaire-2 into Italian Language.J Clin Med. 2025 Apr 24;14(9):2949. doi: 10.3390/jcm14092949. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40363982 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

